Contents
- 1 Introduction to NetSuite ERP Review
- 2 Key Features of NetSuite ERP
- 2.1 1. Financial Management
- 2.2 2. Inventory and Supply Chain Management
- 2.3 3. Business Intelligence and Reporting
- 2.4 4. Customisation and Integration
- 2.5 5. CRM
- 2.6 7. Global Capabilities in NetSuite
- 2.7 8. Human Capital Management (HCM) in NetSuite
- 2.8 9. NetSuite Mobile App Features & Use Cases
- 2.9 10. NetSuite Partner Ecosystem & Implementation Models
- 3 NetSuite Pricing and Licensing Model
- 4 Pros and Cons of NetSuite Worth ERP
- 5 Real User Feedback of the Netsuite Customer
- 6 Suitability for Different Business Sizes and Industries Experience
- 7 Comparison to Other ERP Solutions
- 8 Implementation Best Practices
- 9 Conclusion
Introduction to NetSuite ERP Review
1. Overview of Oracle NetSuite ERP
Brief background on NetSuite and its place in the ERP market
NetSuite, founded in 1998, is renowned for being one of the first companies to offer business applications purely through the cloud. Over the years, it has grown into a full-featured Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platform that caters to organisations of all sizes. Oracle’s acquisition of NetSuite in 2016 further strengthened its position, allowing it to leverage Oracle’s resources to expand globally.
In the ERP market, NetSuite stands out as a pioneer in cloud-based solutions. While many established ERP providers built their initial systems on on-premises models and later transitioned to the cloud, NetSuite was built for the cloud from the outset, making it a leader in modern business management. This approach helped NetSuite carve out a significant share of the market, particularly among growing mid-market organisations and enterprise subsidiaries looking for modern, scalable solutions.
Key selling points or unique attributes
- End-to-end cloud solution: NetSuite’s native cloud architecture provides a single suite of applications covering financials, CRM, e-commerce, inventory, and more, removing the need for multiple on-premises systems.
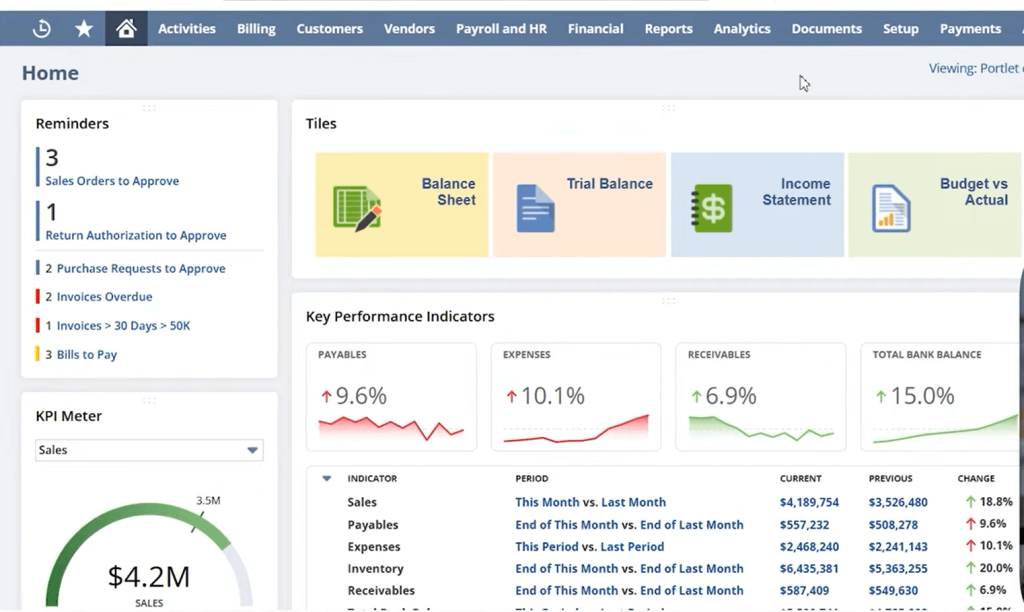
- Real-time visibility and insights: Through customisable dashboards, NetSuite offers real-time reporting and analytics, enabling stakeholders to quickly make data-driven decisions.
- Global reach: Multinational businesses benefit from multi-currency and multi-language support, as well as built-in compliance tools for various international standards.
- Scalability and flexibility: Whether a startup or a large enterprise subsidiary, NetSuite’s modular nature allows organisations to activate additional features as they grow or adapt to new business requirements.
- Ease of integration: NetSuite is designed to integrate well with other systems and third-party applications, simplifying data exchange across the organisation and enhancing overall business management.
2. Why Consider NetSuite ERP?
Common reasons businesses look for comprehensive ERP solutions
- Inefficient legacy systems: Many organisations find themselves relying on outdated software or numerous disconnected tools, resulting in data silos, manual workarounds, and poor visibility.
- Need for real-time data: Modern businesses operate in dynamic environments, and the capability to access up-to-date data on sales, inventory, and financials can be critical for making timely, accurate decisions.
- Regulatory compliance and reporting: Growing enterprises must stay compliant with ever-changing regulations across different regions and industries. Comprehensive ERP solutions simplify tracking and reporting.
- Desire for operational efficiency: A single, centralised ERP solution like NetSuite often automates repetitive tasks and standardises processes, freeing employees to focus on strategic initiatives.
How NetSuite’s cloud-based approach stands out
- Minimal upfront infrastructure costs: Because NetSuite is delivered via the cloud, businesses do not need to invest heavily in servers, data centres, or complex on-premises deployments.
- Automatic updates and innovations: NetSuite rolls out regular updates and new features automatically, ensuring businesses remain on the cutting edge without major upgrade projects.
- Faster deployment and implementation: Cloud-based solutions typically have shorter implementation timelines compared to traditional ERPs, allowing organisations to achieve ROI faster.
- Accessible from anywhere: Users can log in from any location, fostering greater collaboration across distributed teams and enabling remote work.
- Scalable pricing model: NetSuite’s subscription pricing can align with an organisation’s size, usage needs, and growth stages, providing flexibility and cost control.
3. Importance of ERP systems in modern small businesses
ERP systems are crucial for businesses in today’s fast-paced, data-driven world for several reasons:
- Centralised data management: By consolidating data across finance, operations, sales, and other departments, ERPs break down traditional organisational silos. This ensures consistency and reliability in the information that decision-makers rely upon.
- Enhanced process efficiency: Standardised workflows, automated processes, and cohesive reporting reduce human errors and operational bottlenecks. This leads to more streamlined day-to-day activities.
- Improved decision-making: Real-time analytics and dashboards provide key insights into business performance, allowing leadership to identify trends, allocate resources effectively, and respond quickly to market changes.
- Regulatory and compliance support: With built-in compliance reporting tools and audit trails, ERPS help organisations avoid penalties and ensure adherence to regional and industry-specific regulations.
- Scalability to support growth: As businesses expand organically or through acquisitions, a robust ERP system can quickly adapt to new operational complexities, including additional facilities, staff, and product lines.
4. How Does NetSuite Work?
NetSuite is a cloud-based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platform that integrates all core business functions such as accounting, inventory, customer relationship management (CRM), eCommerce, and HR into a single, unified system. Here’s how it works:
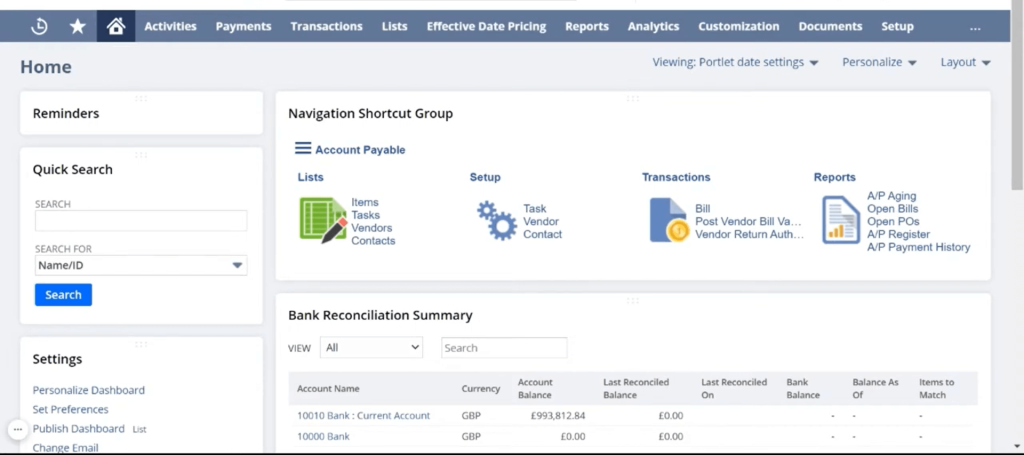
- Centralised Data Management: NetSuite creates a single source of truth by connecting different departments through one database. This eliminates silos and ensures real-time visibility across the business.
- Modular Architecture: Businesses can start with the core ERP and add modules like Supply Chain Management, Human Capital Management, or Project Management as they grow.
- Cloud-Native Deployment: Being fully cloud-based, NetSuite doesn’t require on-premise hardware or installations, making it a cost-effective accounting solution for many businesses. All updates, backups, and security are handled by NetSuite, ensuring scalability and remote access.
- Automation & Workflows: NetSuite automates manual tasks such as billing, revenue recognition, inventory tracking, and reporting. Custom workflows can be set up to match specific business processes.
- Real-Time Analytics & Dashboards: Users get access to customisable dashboards, KPI tracking, and real-time reports, helping decision-makers stay informed and proactive.
- Role-Based Access: Teams get personalised views and access based on their roles, keeping sensitive data secure while empowering each department with what they need.
5. NetSuite’s Target Market
NetSuite is designed for growing businesses and large enterprises across a wide range of industries. Its ideal customers typically face complex operational challenges or are scaling rapidly. Key target segments include:
Mid-Sized to Large Businesses
Especially those outgrowing entry-level tools like QuickBooks or managing multiple systems that don’t talk to each other.
Industries Served:
- Manufacturing & Distribution (inventory, supply chain, demand planning)
- Retail & eCommerce (omnichannel management, order fulfilment)
- Software & SaaS (subscription billing, revenue recognition)
- Professional Services (project accounting, resource planning)
- Nonprofits (grant tracking, fund accounting)
Global Organisations
Companies with international operations benefit from NetSuite’s multi-currency, multi-language, and multi-subsidiary support.
Growth-Minded Companies
NetSuite is ideal for companies planning to scale, expand internationally, or prepare for IPOs thanks to its flexibility and compliance capabilities.
Key Features of NetSuite ERP
1. Financial Management
NetSuite’s Financial Management suite is a robust, cloud-based solution designed to handle the core accounting and financial needs of organisations ranging from small and mid-sized businesses to larger, globally distributed enterprises. By centralising critical financial data and automating key processes, NetSuite helps reduce errors, increase efficiency, and provide real-time visibility into financial performance. Below is an in-depth look at the key components and benefits of NetSuite’s Financial Management capabilities.
Key Components and Benefits
1. Core Financial Modules
1.1 Billing and Invoicing
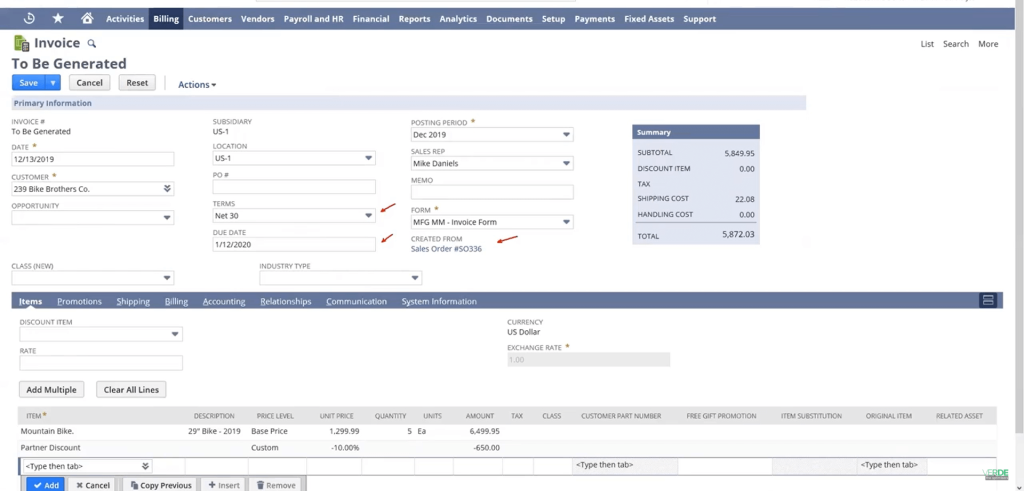
- Multiple Revenue Models: Whether your business follows a subscription model, usage-based model, or one-time fee structure, NetSuite adapts to accommodate different types of billing scenarios.
- Recurring Invoicing: Automate the generation of recurring invoices (e.g., monthly or quarterly), reducing manual tasks and ensuring timely billing cycles.
- Revenue Recognition Compliance: NetSuite aligns with ASC 606 and IFRS 15 standards, ensuring revenue is recognised correctly. The system automatically allocates revenue to the right periods and handles complex scenarios like deferred revenue and multi-element arrangements.
1.2 Multi-Currency and Global Support
- Automatic Currency Conversions: For organisations operating in multiple countries, NetSuite simplifies transactions with automatic currency conversions, real-time exchange rate updates, and currency revaluation features.
- Consolidated Financial Statements: NetSuite’s multi-entity management allows parent companies to consolidate reports across subsidiaries, applying intercompany eliminations and converting all data into a single reporting currency.
- Localised Tax and Regulatory Compliance: Built-in tax management features support diverse tax codes, while country-specific compliance modules ensure alignment with regional regulations (e.g., VAT, GST).
2. Financial Reporting and Performance Evaluation
NetSuite’s Financial Reporting suite provides comprehensive, real-time insights into a company’s financial health. Finance teams and executives can assess the organisation’s performance quickly and accurately, helping them make data-driven decisions.
2.1 Key Financial Statements
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
- Automated Revenue & Expense Tracking: NetSuite pulls data directly from subledgers, ensuring accuracy and timeliness.
- Department/Project-Level Insights: Drill down into specific departments or projects to see precisely where profits or losses are coming from.
- Comparative Analysis: Easily compare current results against historical periods, budgets, or forecasts to spot trends and variances.
Balance Sheet
- Up-to-Date Asset and Liability Balances: Every financial transaction updates the relevant balance sheet accounts in real time.
- Customisable Reporting Views: Group accounts or create custom classifications to align with unique business needs or compliance standards in your accounting software.
- Multi-Entity Consolidation: For businesses with subsidiaries, NetSuite’s automated consolidation features simplify the creation of consolidated balance sheets.
Cash Flow Statement
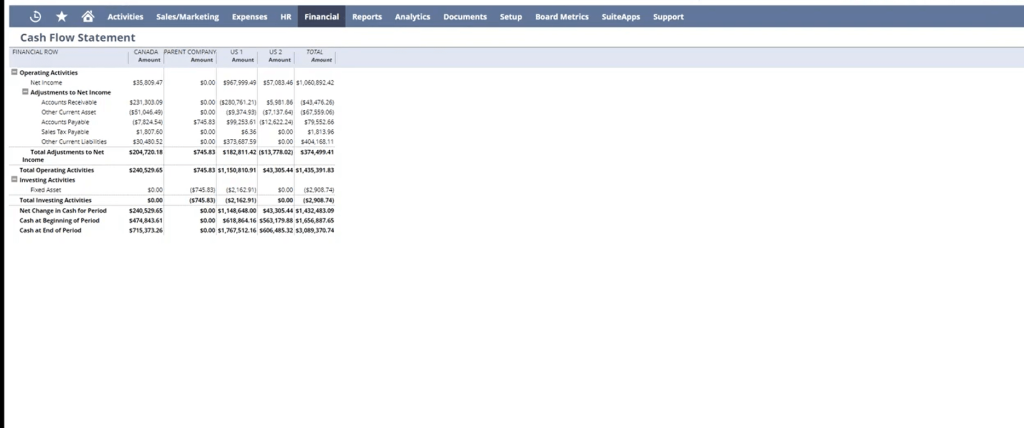
- Real-Time Cash Monitoring: Track cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Direct & Indirect Methods: NetSuite supports both methods to comply with regional accounting preferences and regulations.
- Cash Forecasting: Use historical data alongside current transactions to project future cash positions, aiding in capital planning and budgeting.
2.2 Performance Dashboards and KPIs
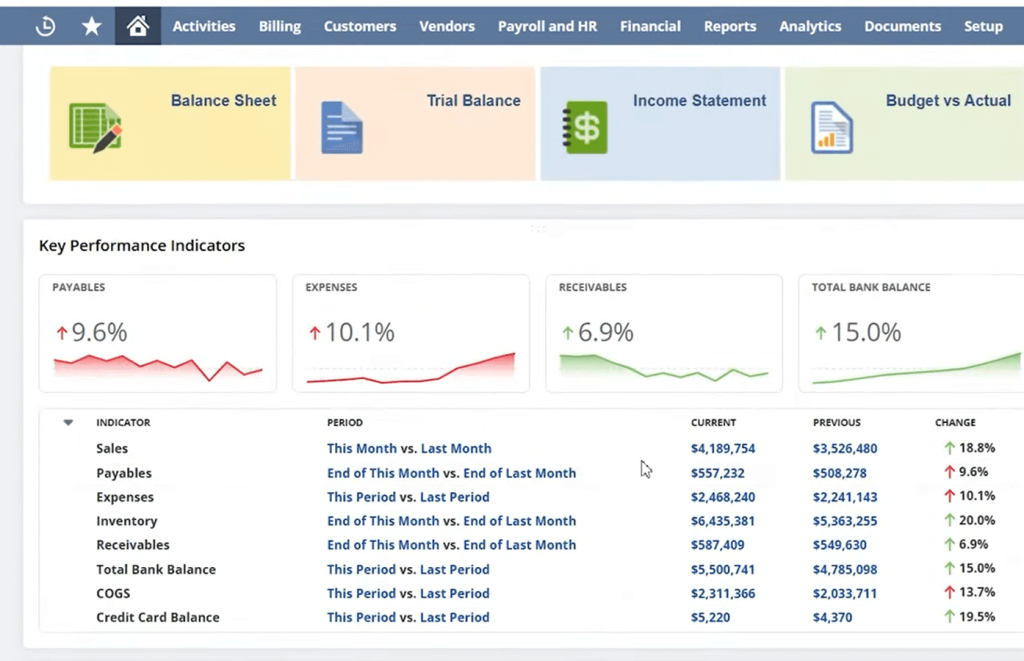
- Role-Based Dashboards: Tailored views for CFOS, controllers, and other stakeholders ensure that the most relevant metrics appear at login.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): NetSuite offers out-of-the-box KPIs (e.g., DSO, Gross Margin, etc.) and allows custom KPI for organisation-specific insights.
- Drill-Down Functionality: Quickly move from a high-level summary into specific transaction details, speeding up financial analysis and issue resolution.
3. Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)
NetSuite’s FP&A features allow finance teams to go beyond basic reporting and into strategic planning. By harnessing historical data and forward-looking forecasts, organisations can align budgets, predict performance, and respond proactively to market changes.
3.1 Budgeting
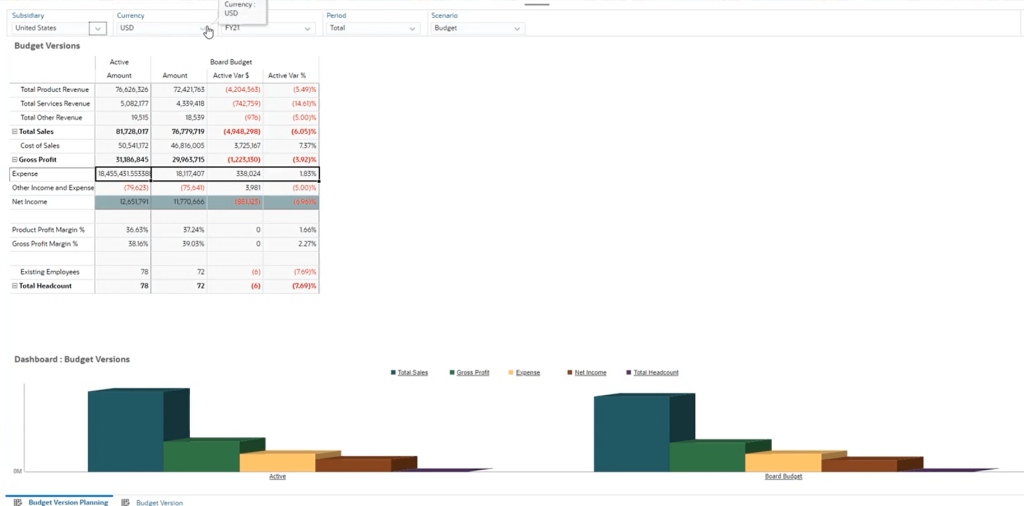
- Multi-Level Budget Creation: Develop budgets at the company, department, project, or subsidiary level. This granular approach offers a deeper understanding of financial constraints and goals.
- Variance Analysis: Compare actual results against budgeted figures in real-time. NetSuite flags areas of over- or under-spending, helping stakeholders address issues quickly.
- Collaboration Tools: Enable cross-functional teams to contribute to budget planning and revision, all within the same platform.
3.2 Forecasting

- Rolling Forecasts: Continuously update forecasts as new data enters the system, avoiding static or outdated projections.
- What-If Scenario Analysis: Model the financial impact of hypothetical changes such as adding a new product line, entering a new market, or modifying pricing structures to make informed decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: NetSuite’s ERP offers advanced predictive analytics capabilities to enhance business management. Integrate NetSuite data with external Business Intelligence tools or leverage built-in analytics to refine forecast accuracy using historical trends and patterns.
4. Compliance, Audit, and Security
A key advantage of NetSuite’s Financial Management platform is its emphasis on compliance and security. Robust controls, documentation features, and automated workflows simplify auditing and reduce the risk of fraud or noncompliance.
- Audit Trails: Every transaction and change within the system is tracked, detailing user actions and timestamps. This facilitates easier internal and external audits.
- Role-Based Permissions and Approvals: Assign permissions based on job functions, ensuring that only authorised personnel can view or modify sensitive data.
- Regulatory Compliance Tools: Built-in templates and disclosures for various regulations (e.g., GAAP, IFRS) in accounting software accelerate reporting. These tools also ease compliance with tax requirements in multiple regions.
2. Inventory and Supply Chain Management
NetSuite’s Inventory and Supply Chain Management modules are designed to streamline the flow of goods, optimise stock levels, and ensure supply chain visibility across global operations. Whether it’s a manufacturing firm, a distributor, or a retail business, NetSuite helps balance demand and supply efficiently.
1. Inventory Management
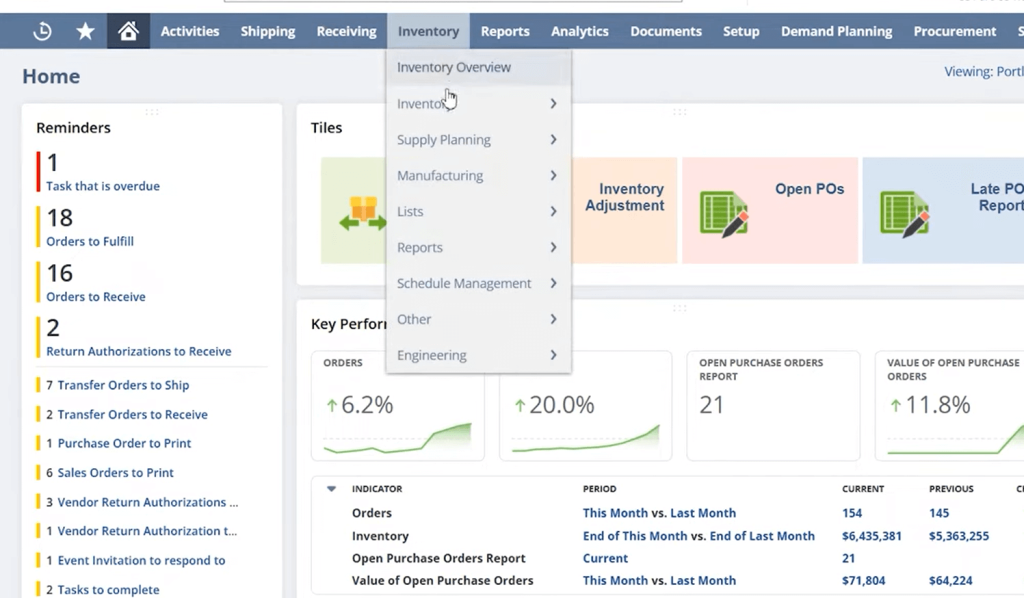
- Real-Time Inventory Visibility: NetSuite provides centralised, real-time visibility into inventory levels across multiple locations, warehouses, and stores. You can track on-hand, committed, and available inventory at any point in time.
- Multi-Location Inventory Control: Manage inventory across various warehouses, distribution centres, retail stores, or even third-party logistics (3PL) partners. NetSuite supports location-specific safety stock, reorder points and lead times.
- Lot and Serial Number Tracking: For businesses that require traceability (like pharmaceuticals, electronics, or food), NetSuite supports lot and serial number tracking from procurement to fulfilment.
- Bin Management: NetSuite enables advanced warehouse management with bin tracking capabilities, allowing for optimised picking, packing, and putaway processes.
- Cycle Counting and Inventory Reconciliation: Automated cycle counting helps maintain inventory accuracy without the need for disruptive full physical counts.
2. Order and Fulfillment Management
- Sales and Purchase Order Automation: Automate the entire order lifecycle from order creation and approval to fulfillment and invoicing, ensuring quick turnaround and minimal manual intervention.
- Drop Shipping and Special Orders: Route specific orders directly from suppliers to customers without holding inventory. Ideal for eCommerce or specialised retail models.
- Fulfilment Workflow Management: NetSuite supports advanced fulfilment rules, including partial shipments, backorders, and multiple shipment locations.
3. Demand Planning and Procurement
- Demand Forecasting: Analyze historical sales, seasonal trends, and other variables to predict future demand. Forecasts feed directly into procurement plans.
- Reorder Point and Safety Stock Automation: Automate procurement triggers based on real-time inventory levels, lead times, and projected demand.
- Vendor Management: Track vendor performance metrics such as delivery time, order accuracy, and cost. NetSuite also supports supplier portals for collaboration and procurement efficiency, providing a comprehensive business software experience.
4. Supply Chain Visibility
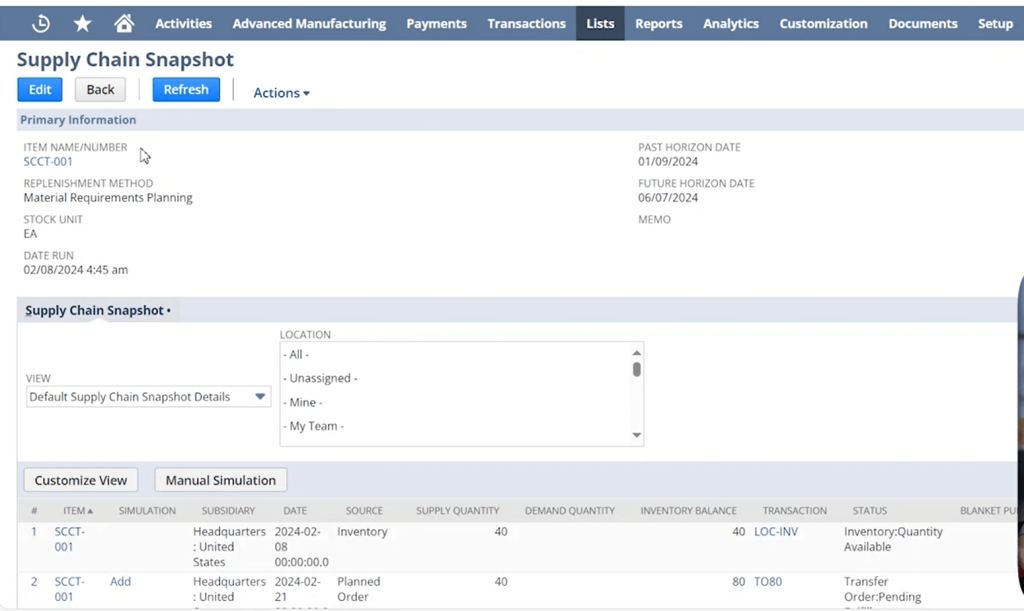
- Real-Time Supply Chain Dashboard: Get a unified view of procurement, production, inventory, and distribution activities. NetSuite’s dashboards highlight KPIs like inventory turnover, order cycle time, and stock-outs.
- Global Supply Chain Support: Manage supply chain activities across global locations, subsidiaries, and currencies with consolidated reporting and compliance controls.
3. Business Intelligence and Reporting
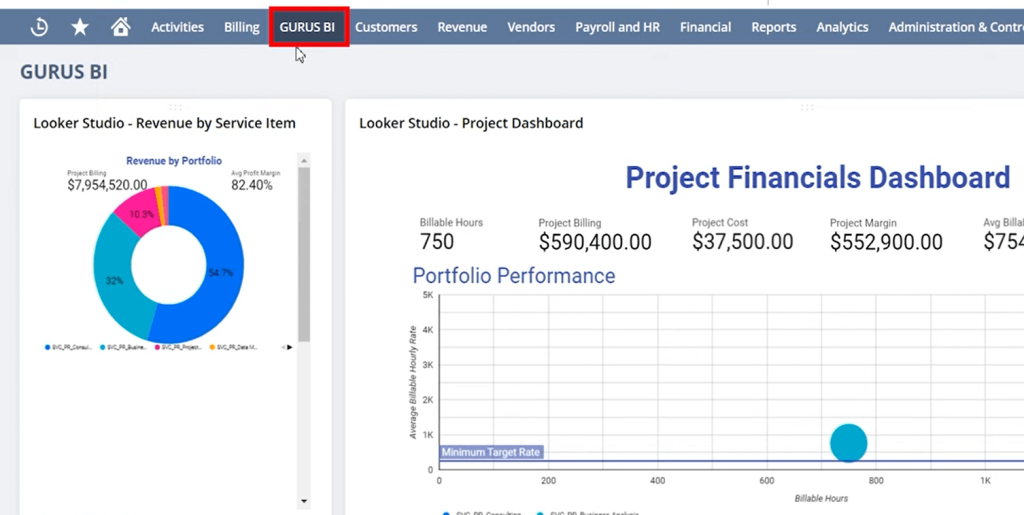
NetSuite’s Business Intelligence (BI) and reporting capabilities are designed to give organisations real-time, data-driven insights into every facet of their operations. By centralising all core business data financials, inventory, sales, marketing, and more, NetSuite empowers users to create dynamic reports, dashboards, and analytics without the need for complex integrations or external tools. Below is a detailed look at the key components and advantages of NetSuite’s BI and reporting features.
1. SuiteAnalytics (Built-in BI Tool)
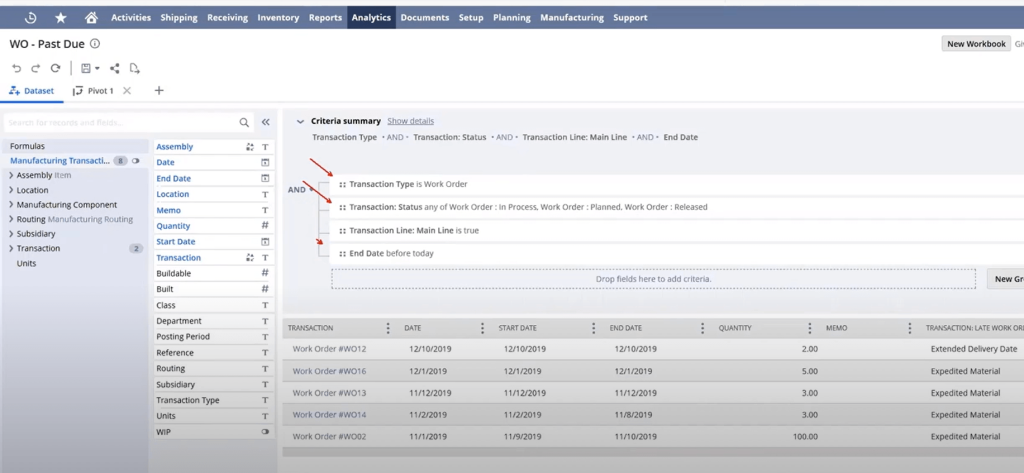
- Real-Time Dashboards: Personalised, role-based dashboards provide instant access to KPIs, reports, charts, and reminders. CFOs, operations managers, and inventory controllers each get a tailored view.
- Saved Searches: Create dynamic queries on virtually any data set in NetSuite. Saved Searches allow users to filter, sort, and display real-time data for granular insights no coding required.
- Suite Analytics Workbook: Offers advanced data exploration using a drag-and-drop interface. Users can build pivot tables, charts, and multi-dimensional reports with ease.
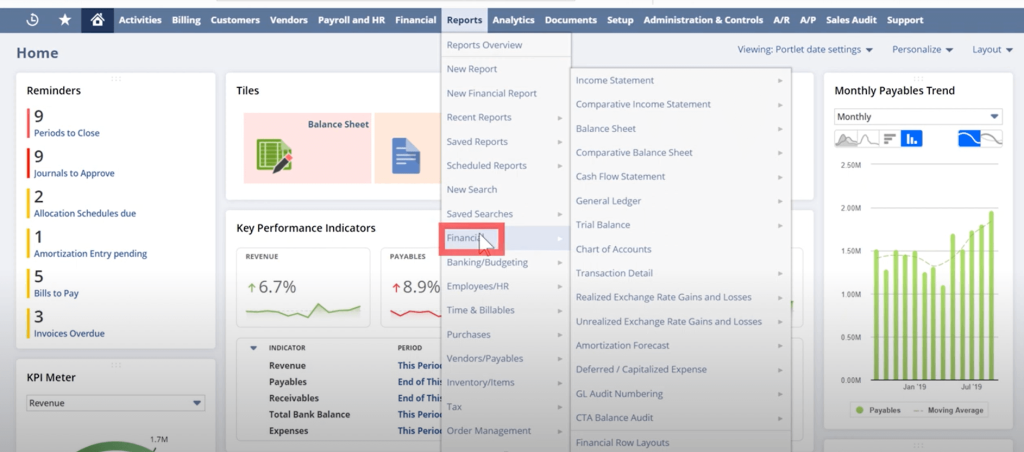
- Pre-Built Reports and Templates: NetSuite includes standard reports for financials, sales, inventory, and operations that can be used as-is or customised as needed.
2. Custom Reporting and KPIs
- Custom Report Builder: Users can design reports tailored to unique business needs by selecting data fields, applying filters, and choosing layout formats.
- Formula Fields & Calculated Metrics: Enhance reports with custom calculations, conditional formatting, or user-defined metrics.
- Drill-Down Functionality: Every dashboard component or report can be drilled down to the transaction level, providing unmatched transparency.
- Automated Report Distribution: Schedule and automatically email reports to internal or external stakeholders at defined intervals, ensuring consistent communication.
3. Advanced Analytics (via Suite Analytics and Add-Ons)
- Trend and Variance Analysis: Analyse changes over time and compare against budgets or forecasts to spot operational inefficiencies or growth opportunities.
- Embedded Analytics: Place contextual analytics directly inside transactional records like invoices or purchase orders so users can make data-driven decisions without switching screens.
- Integration with External BI Tools: For organisations using advanced BI platforms (e.g., Tableau, Power BI, Looker), NetSuite data can be exported or connected via ODBC, JDBC, or REST APIs.
4. Customisation and Integration
Customisation and Integration is one of NetSuite’s most powerful features, enabling businesses to mould the system to their unique workflows and seamlessly connect it with other platforms. This flexibility allows organisations to streamline processes, enhance user experience, and achieve end-to-end visibility across systems without sacrificing upgrade compatibility.
1. Customisation: Tailor NetSuite to Fit Your Business
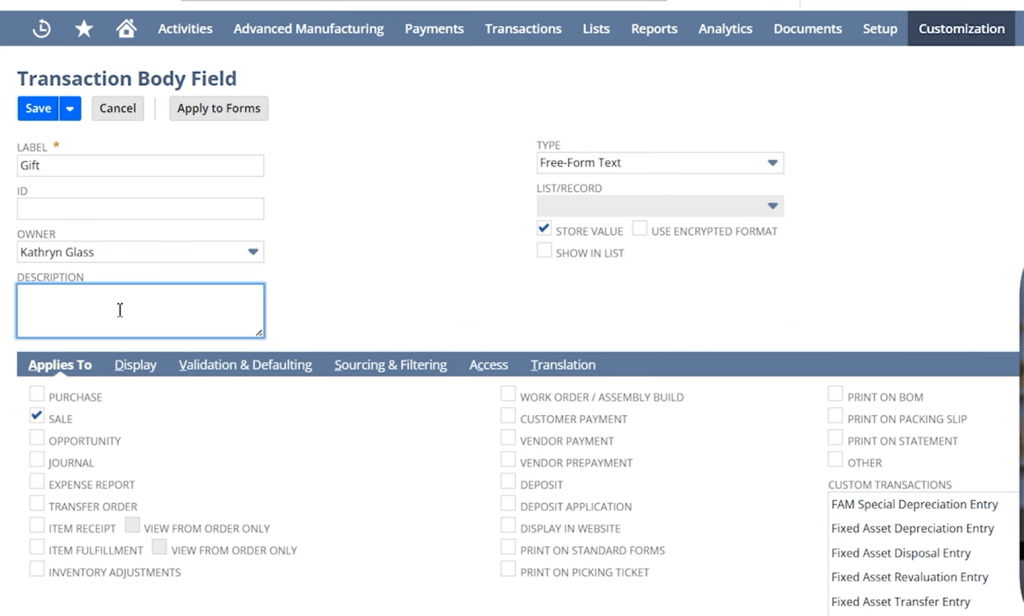
NetSuite provides a suite of tools that allow you to customise nearly every aspect of the system, from data fields to workflows, without touching the core code. These customisations are upgrade-safe and scalable.
a. SuiteBuilder (No-Code/Low-Code Configuration)
SuiteBuilder allows non-technical users and admins to modify the interface and data structure through point-and-click configuration.
- Custom Fields: Add new data fields to forms (e.g., checkboxes, dropdowns, formulas).
- Custom Records: Create entirely new record types to capture business-specific data.
- Custom Forms: Design the layout of entry and transaction forms, controlling visibility and behaviour.
- Custom Tabs and Subtabs: Organise information in a way that suits your teams.
b. SuiteFlow (Workflow Automation)
SuiteFlow is NetSuite’s built-in workflow engine that allows you to automate business processes without writing code.
- Create approval chains, automated email notifications, field updates, or task assignments.
- Trigger workflows on record events (e.g., when a record is created or updated).
- Incorporate conditions, branching logic, and transitions.
c. SuiteScript (Advanced Customisation with JavaScript)
SuiteScript provides developers with programmatic access to NetSuite’s data and logic layer.
- Client Scripts: Trigger interactions in the user interface (e.g., real-time field validation).
- User Event Scripts: Run logic on record creation/update/delete in customizable accounting software solutions.
- Scheduled Scripts: Automate background tasks (e.g., nightly batch processing).
- RESTlets: Create custom REST APIs to expose or receive data.
d. SuiteAnalytics Workbook Customisation
Users can build custom reports, KPIs, and dashboards by leveraging drag-and-drop analytics no SQL required.
- Combine multiple data sources.
- Create pivot tables and charts.
- Share insights securely across departments.
2. Integration: Connect NetSuite with Everything
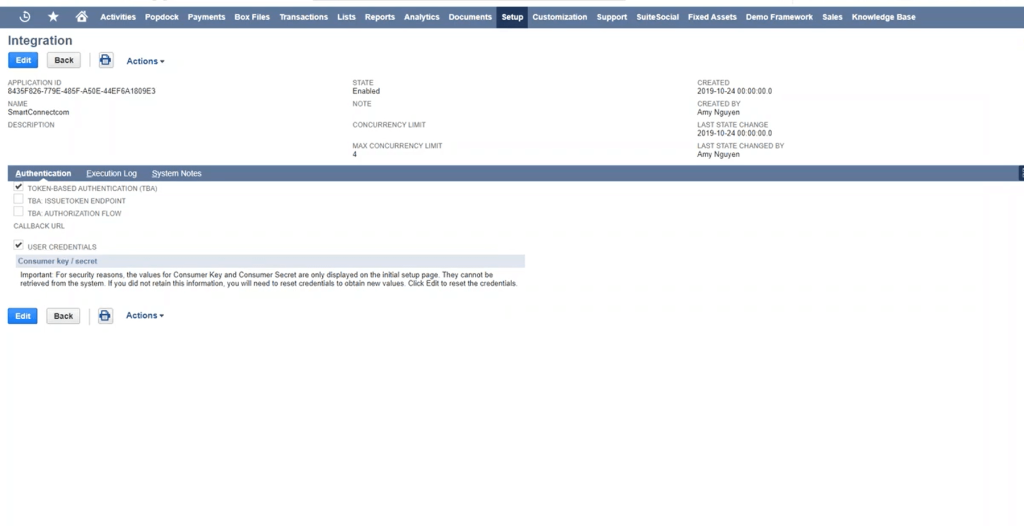
Whether you’re syncing eCommerce orders, pushing financials to BI tools, or integrating with CRM, NetSuite offers a robust ecosystem for integration.
a. SuiteTalk (SOAP and REST Web Services)
SuiteTalk is NetSuite’s official API framework, offering both SOAP and REST protocols.
- Perform CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) on virtually all records.
- Execute saved searches and workflows.
- Secure endpoints via Token-Based Authentication or OAuth 2.0.
Use Cases:
- Sync customer records between NetSuite and Salesforce.
- Push NetSuite invoices into external billing systems.
- Integrate with HR or payroll software.
b. RESTlets (Custom APIs)
For more lightweight or customised integrations, RESTlets allow you to create custom RESTful endpoints via SuiteScript.
- Define exactly how data is sent or received.
- Ideal for mobile apps or real-time syncing with third-party services.
c. SuiteTalk for Excel Add-In
Allows users to pull NetSuite data directly into Excel, manipulate it, and sync back.
- Streamlines financial reporting.
- Enables power users to work in familiar tools.
d. Integration Middleware and Connectors

NetSuite integrates seamlessly with popular third-party platforms and iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) tools.
- Celigo, Dell Boomi, MuleSoft, Jitterbit: Prebuilt connectors for Shopify, HubSpot, Salesforce, Amazon, etc.
- Reduces development time and maintenance.
- Ideal for multi-system, multi-channel businesses.
e. SuiteCloud Development Framework (SDF)
For enterprise-grade teams, SDF allows you to manage all customisations and integrations as code ideal for DevOps workflows.
- Version control (Git, Bitbucket).
- CI/CD pipeline ready.
- Package and deploy customisations across NetSuite accounts.
5. CRM
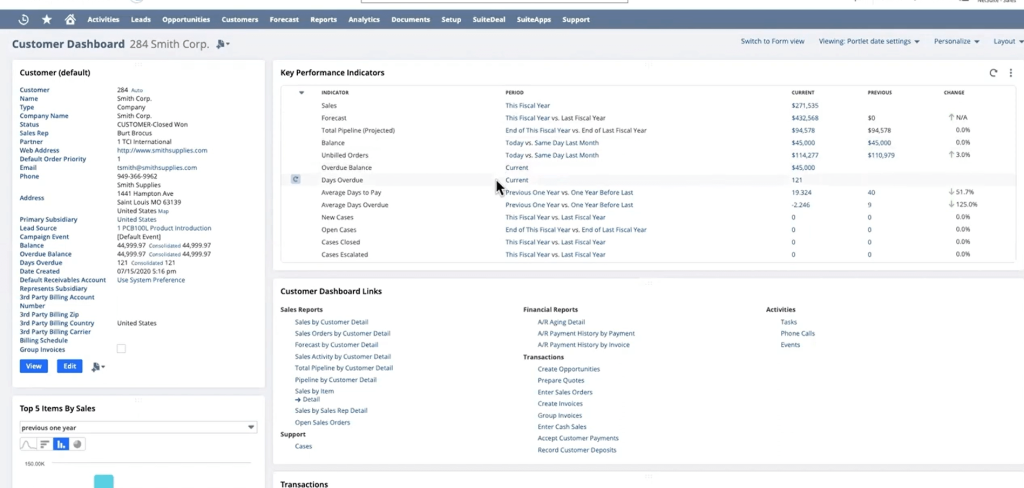
NetSuite CRM (Customer Relationship Management) helps you acquire, engage, and retain customers in a single, integrated platform. By unifying marketing, sales, and service data, NetSuite CRM delivers real-time visibility into every interaction with your prospects and customers.
Key Components of NetSuite CRM
1.1 Lead and Opportunity Management
- Lead Capture: Automatically capture leads from website forms, marketing campaigns, or partner referrals.
- Lead Qualification: Score and qualify leads based on criteria like industry, lead source, and engagement.
- Opportunity Tracking: Convert qualified leads into opportunities, track deal stages, estimated close dates, and potential revenue.
1.2 Sales Force Automation (SFA)
- Pipeline Visibility: Gain insight into the entire sales pipeline, from early leads to closed deals.
- Activity Management: Log calls, emails, tasks, and meetings directly into the CRM record.
- Quoting and Order Management: Create quotes and sales orders directly from the opportunity record with no duplication of data.
- Sales Forecasting: Predict revenue with real-time accuracy. Roll up forecasts by sales rep, region, or product line.
1.3 Marketing Automation
- Campaign Creation and Execution: Plan, execute, and track email campaigns, webinar promotions, or direct mail.
- Lead Nurturing: Automate multi-step drip campaigns to move leads through the funnel.
- Segmentation and Targeting: Filter prospects by demographics, purchase history, or online behaviour.
- ROI Tracking: Link marketing spend to closed deals for a full picture of campaign effectiveness.
1.4 Customer Service and Support
- Case Management: Convert emails, calls, and website inquiries into cases. Assign to support reps automatically or manually.
- Knowledge Base: Store articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides. Empower both customers (via self-service) and support teams.
- Service-Level Agreements (SLAs): Track response and resolution times, ensuring adherence to customer contracts.
- Support Analytics: Measure first-call resolution, average response time, and ticket volume trends.
1.5 Partner Relationship Management (PRM)
- Partner Portal: Provide a dedicated interface for your partners to register deals, track opportunities, and access marketing materials.
- Deal Registration: Partners can register leads to avoid channel conflicts and ensure accurate tracking.
- Co-marketing Programs: Extend marketing campaigns to partners, and track joint pipeline and ROI.
- Real-Time Communication: Share real-time data on leads, orders, and commission statements with your channel partners.
1.6 Mobile Access
- NetSuite Mobile App: Access CRM data on smartphones and tablets. View customer records, manage tasks, and log calls on the go.
- Offline Functionality: Work offline with cached records and sync updates once you’re back online.
7. Global Capabilities in NetSuite
NetSuite’s Global Capabilities empower multinational companies to operate seamlessly across borders. Whether you’re managing subsidiaries, handling multi-currency transactions, or ensuring compliance with regional tax laws, NetSuite delivers a unified cloud platform designed to handle the complexities of global business in real-time, and at scale.
1. Multi-Subsidiary Management with OneWorld
NetSuite OneWorld is the core engine behind its global functionality. It allows organisations to manage multiple legal entities, business units, and subsidiaries within a single NetSuite account.
Key Features:
- Consolidated Financials: Automatically roll up financials from subsidiaries to headquarters in real-time, accurate, and currency-adjusted.
- Subsidiary Segmentation: Create and manage different business units with separate books, tax rules, and currencies.
- Local and Global Reporting: View financials at both local and consolidated levels.
- Intercompany Transactions: Automate intercompany sales, billing, and eliminations.
2. Multi-Currency Transactions
Operate in multiple currencies without manual conversions or siloed systems.
- Automatic Currency Conversion: Real-time exchange rates via integration with global rate providers.
- Multi-Currency Price Lists: Define pricing rules for each region or customer group.
- Currency Revaluation: Automate the month-end revaluation of foreign balances for financial compliance.
- Support for Over 190 Currencies: This allows businesses to conduct transactions and manage financial data in a wide range of currencies, including those defined by ISO 4217.
3. Multi-Language and Localisation Support
NetSuite supports over 27 languages, allowing users to interact with the system in their native language.
- Language Preferences by User: Each employee, vendor, or partner can set their preferred language in customisable settings.
- Localised Forms and PDFs: Customise invoices, purchase orders, and other transaction documents by country or region.
- Localisation Packs: Country-specific bundles that include tax codes, chart of accounts templates, and regulatory formats.
4. Global Time Zones and Calendars
Operate and report across time zones effortlessly.
- Time Zone Support: Automatically adjust for time zone differences when scheduling workflows, approvals, or campaigns.
- Multi-Calendar Support: Accommodate differing fiscal calendars across subsidiaries and consolidate seamlessly at HQ.
5. Global Reporting and Analytics
Make smarter decisions with real-time visibility across your global operations.
- Real-Time Dashboards: View subsidiary performance, intercompany metrics, or global KPIs from a unified interface.
- Custom Reports and Saved Searches: Drill down into regional sales, inventory, compliance metrics, and more.
- Role-Based Access: Ensure users only see data relevant to their region, function, or subsidiary.
8. Human Capital Management (HCM) in NetSuite
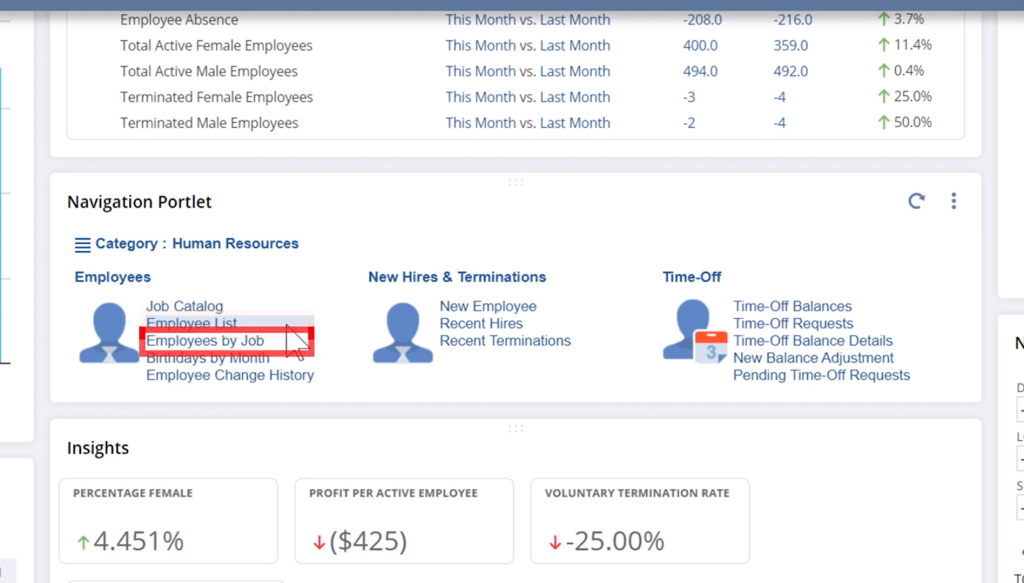
NetSuite Human Capital Management (HCM) also referred to as SuitePeople, is NetSuite’s fully integrated solution for managing your workforce. It’s designed to streamline HR operations, improve employee engagement, and align your people strategy with business growth.
NetSuite HCM / SuitePeople?
SuitePeople is NetSuite’s cloud-based HR management system that sits natively within the NetSuite ERP platform. Unlike third-party HR systems that require complicated integrations, SuitePeople works seamlessly with your financials, payroll, projects, and other business processes giving you a unified platform for your people and your operations.
Key Features of NetSuite HCM
1. Core HR & Employee Records
- Maintain a centralised, secure record for every employee.
- Track demographics, job roles, departments, employment history, and more.
- Integrated with workflows and approvals for hiring, transfers, and terminations.
2. Employee Self-Service Portal
- Employees can update their personal info, submit time-off requests, and view payslips all in one place.
- Reduces administrative workload for HR teams.
3. Payroll Management (US only – with some third-party options globally)
- Fully integrated payroll engine with automated tax calculations, direct deposits, and compliance.
- Syncs directly with GL and financial reporting for accurate headcount-related expenses.
4. Time-Off and Leave Management
- Automate accruals, leave policies, and approvals.
- Managers can track availability and handle approvals through dashboards.
5. Performance Management
- Set goals, manage employee reviews, and conduct regular performance assessments.
- Align individual goals with company objectives for better engagement and accountability.
6. Workforce Analytics
- Gain insights into workforce trends like turnover, headcount growth, compensation trends.
- Prebuilt and customisable reports help HR and executives make data-driven decisions.
7. Org Management
- Visual org charts and position management help you plan staffing and manage reporting hierarchies.
9. NetSuite Mobile App Features & Use Cases
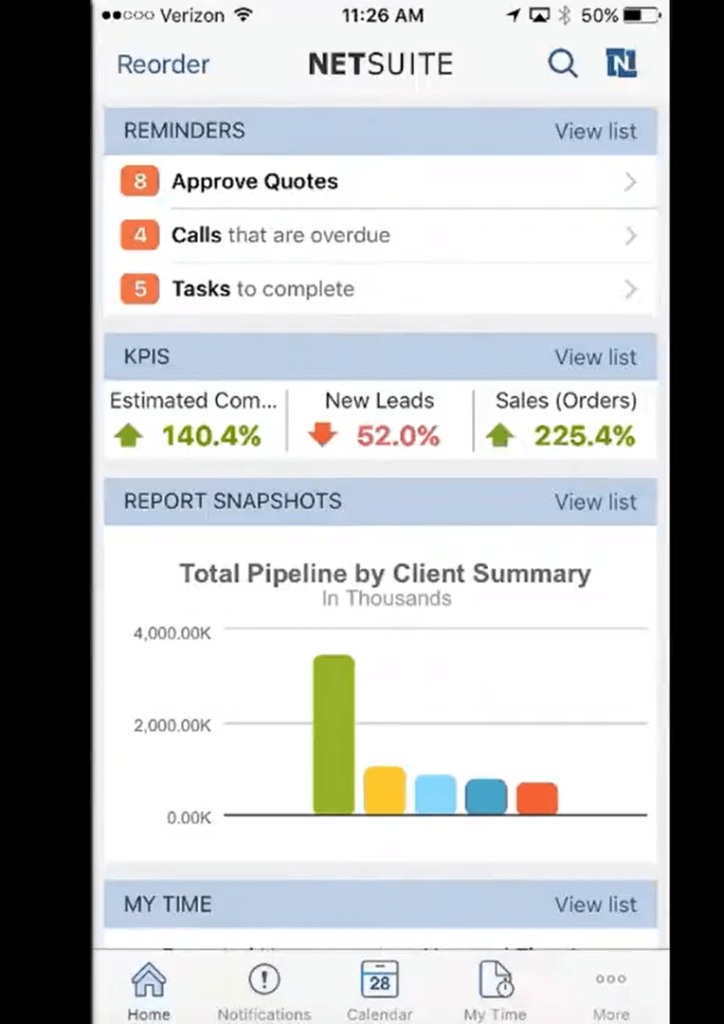
Many decision-makers today seek ERP mobility to manage business processes on the go. NetSuite delivers a mobile app that brings essential ERP functionality directly to users’ fingertips, whether they’re in the office, on-site, or traveling.
Key Features of the NetSuite Mobile App:
- Real-Time Dashboards: Access key metrics and KPIs instantly through role-based dashboards.
- Offline Functionality: View and update records offline, with automatic syncing once reconnected to the internet, enhancing the overall business solutions offered by NetSuite.
- Workflow Approvals: Approve purchase orders, timesheets, or journal entries from anywhere.
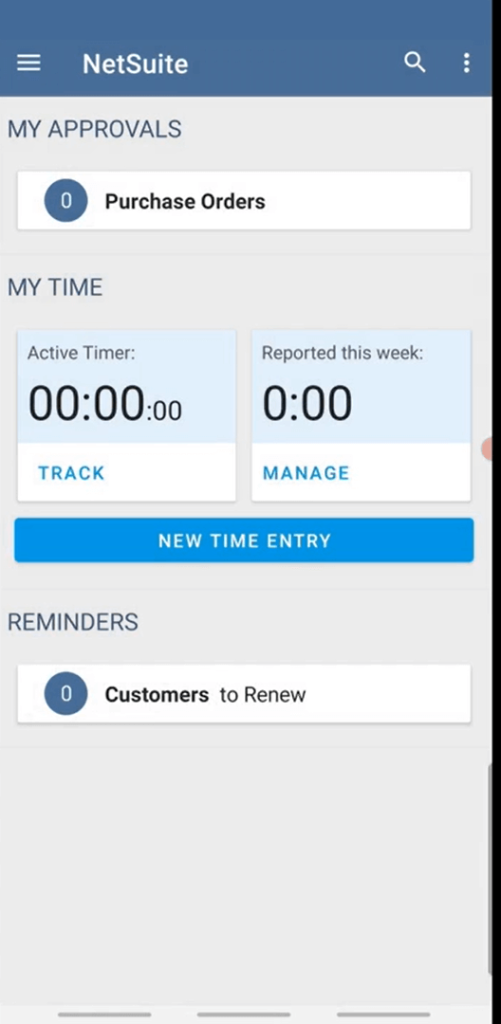
- Task & Activity Management: Users can log calls, update opportunities, and manage their daily schedules.
- Customer and Vendor Access: View contact records, recent interactions, transaction histories, and notes.
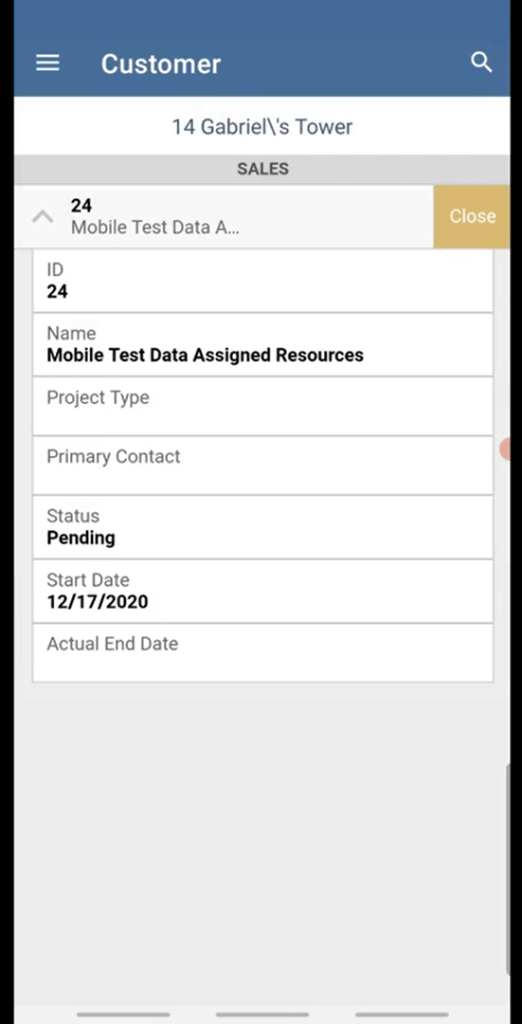
Ideal Use Cases:
- Sales Representatives: Review leads, enter orders, or log activities while on client visits.
- Executives: Monitor high-level dashboards and approve time-sensitive requests during travel.
- Warehouse or Field Staff: Use mobile scanning and fulfilment tools (with compatible integrations) to streamline inventory tasks.
The app is available on both iOS and Android, designed with a responsive UI that adapts to tablet and phone screens. By offering a connected and secure mobile ERP experience, NetSuite helps modern businesses stay agile and productive from virtually anywhere.
10. NetSuite Partner Ecosystem & Implementation Models
Oracle NetSuite’s expansive partner ecosystem plays a pivotal role in delivering its cloud ERP solution across industries and geographies. From specialised solution providers to third-party SuiteApp developers, the ecosystem adds tremendous value during implementation and post-go-live support.
Let’s explore how NetSuite deployments differ when done directly through Oracle versus with a partner, how to evaluate the right solution provider, and which third-party SuiteApps are most popular for enhancing your NetSuite experience.
Direct vs. Partner-led Implementations
NetSuite offers two primary implementation pathways:
1. Direct Implementation (Oracle-led)
This approach is handled by NetSuite’s internal professional services team. It often suits mid-to-large enterprises with complex, multi-entity structures or global operations.
Pros:
- Deep product expertise
- Close alignment with the NetSuite product roadmap
- Fast-track onboarding via SuiteSuccess methodology
Cons:
- Less customisation flexibility
- Higher cost compared to smaller partners
- Limited hand-holding after go-live
2. Partner-led Implementation
NetSuite partners, including Solution Providers, Alliance Partners, and SDN (SuiteCloud Developer Network) partners, offer tailored implementations, industry-specific templates, and localised support.
Pros:
- More personalised service
- Flexible pricing and timelines
- Industry specialisation (e.g., retail, manufacturing, SaaS)
- Often includes value-added services like custom integrations, training, or ongoing admin support
Cons:
- Quality varies between partners vetting is essential
- Some smaller partners may lack experience with complex setups
How to Choose a NetSuite Solution Provider
| Factor | What to Look For |
| Industry Expertise | Does the partner specialise in your sector (e.g., manufacturing, nonprofit, eCommerce)? |
| NetSuite Certifications | Look for Certified NetSuite ERP Consultants, Developers, and SuiteFoundation credentials. |
| Implementation Track Record | Ask for case studies, customer references, and number of completed implementations. |
| Geographic Reach | Do they support your region/time zone? Crucial for multi-country rollouts. |
| Post-Go-Live Support | Do they offer admin-as-a-service or managed services after deployment? |
| SuiteApps/Custom Solutions | Some partners build their own add-ons—do these align with your needs? |
Tip: Shortlist partners listed on NetSuite’s official Partner Finder and check for Verified Reviews on G2 or TrustRadius.
Popular Partner-Built SuiteApps
The NetSuite SuiteCloud platform allows partners to build tailored applications known as SuiteApps that integrate natively with NetSuite. These apps address industry-specific gaps and improve workflow efficiency.
Here are a few widely adopted SuiteApps built by NetSuite partners:
ZoneBilling (by Zone & Co)
- Purpose: Advanced subscription billing and revenue recognition for SaaS and subscription-based businesses.
- Why it’s popular: Automates ASC 606/IFRS 15 compliance and supports complex billing models like usage-based or milestone-based billing.
RF-SMART
- Purpose: Real-time mobile inventory and warehouse management for NetSuite.
- Why it’s popular: Improves picking, packing, shipping, and cycle counting with barcode scanning and mobile capabilities.
Celigo Integrator.io
- Purpose: iPaaS platform for integrating NetSuite with external systems (e.g., Shopify, Salesforce, Amazon).
- Why it’s popular: Drag-and-drop integration builder with prebuilt templates for rapid deployment.
FloQast
- Purpose: Close management software that complements NetSuite’s financials.
- Why it’s popular: Enables faster month-end close and better audit trail management, especially for accounting teams, according to many NetSuite reviews.
Pacejet
- Purpose: Multi-carrier shipping and logistics management.
- Why it’s popular: Seamlessly connects with FedEx, UPS, DHL, and freight carriers to optimise shipping rates and delivery times.
NetSuite Pricing and Licensing Model
Below is a detailed explanation of how NetSuite pricing typically works, reflecting the most common structures and considerations. While exact pricing figures will vary from customer to customer and are often negotiated on a per-contract basis the following overview provides general insights into NetSuite’s licensing model, key cost drivers, and implementation considerations.
1. Subscription-Based Licensing
Overview of NetSuite’s SaaS Approach
NetSuite follows the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, meaning you access the system via the cloud rather than installing it on your own servers. You effectively “rent” the software and receive updates, security patches, and new features as part of your subscription. This approach lets companies avoid large upfront capital expenditures associated with on-premise hardware and software.
Monthly/Annual Subscription Options
- Billing Periods: Most NetSuite contracts run on annual terms. However, some customers may negotiate multi-year or monthly billing cycles (rare but sometimes offered through partners or special arrangements).
- Subscription Tiers: You pay for specific modules/functionality (e.g., CRM, ERP, OneWorld, SuiteCommerce) and the number of “seats” (named user licenses or employee users) needed in your organisation.
Key Benefit: The subscription model ensures predictable operational expenses rather than large, one-time capital investments.
2. Factors Affecting Cost
Number of Users, Modules, and Subsidiaries
User Count: You pay for the number of user licenses needed to access NetSuite’s ERP. Larger organisations with more employees/roles accessing NetSuite will incur higher subscription fees.
Modules/Products: NetSuite offers various core and advanced modules (e.g., Advanced Financials, Advanced Revenue Management, SuiteProjects for PSA, etc.). Each module you add typically increases your monthly/annual subscription cost.
Subsidiaries (OneWorld): If you have international or multi-entity needs, OneWorld functionality is essential. This typically adds an incremental cost for each subsidiary or entity managed within NetSuite.
Customisations and Add-Ons
SuiteApps: NetSuite’s marketplace (SuiteApp.com) provides third-party applications that integrate directly into NetSuite. Some are free, while others require additional licensing or subscription fees.
Custom Fields and Scripts: Simple customisations (e.g., custom fields, forms, workflows) usually do not directly add to your NetSuite subscription cost, but certain advanced scripts or heavy usage might require higher service tiers or additional governance considerations.
Advanced Functionality: If you need advanced modules such as Demand Planning, Warehouse Management, or specialised integrations, these come at an additional cost.
Pro Tip: Work with your NetSuite account representative or partner to identify which modules are truly necessary versus “nice to have,” as each additional module impacts your subscription fee.
3. Implementation and Services
Professional Services Costs (Training, Customisation, Data Migration)
- Initial Implementation: A NetSuite implementation typically involves scoping, project planning, setup, data migration, and testing. The cost can vary widely, from smaller projects (in the tens of thousands of dollars) to larger, more complex rollouts (potentially well into six figures).
- Customisation: If you require advanced custom scripts (SuiteScript) or intricate workflows (SuiteFlow), you’ll either need to hire a NetSuite partner or maintain in-house developers. This can drive up professional service fees.
- Training and Change Management: Training end users and administrators can be done via NetSuite’s or a partner’s training programs, often billed per course or as part of a consulting package.
Ongoing Support Fees
- Customer Support Tiers: NetSuite offers different support levels (e.g., Basic, Premium, Advanced). Each level affects the speed of response, dedicated support contacts, and coverage hours in NetSuite’s user-friendly ERP software.
- Partner-Provided Support: Some customers rely on NetSuite Solution Providers or Alliance Partners for day-to-day support. These partners might charge a retainer or hourly rate for ongoing assistance.
- Upgrades and Maintenance: Since NetSuite is cloud-based, system upgrades are included in the subscription. However, ensuring custom scripts continue to function post-upgrade may require additional testing and developer effort.
NetSuite Release Schedule & Upgrade Cycle
Helpful for mid-size and enterprise IT teams:
- Twice-yearly updates
- Sneak peeks or tips on preparing for major releases can enhance the experience with NetSuite for its users.
- How upgrade-safe customisations work
Pros and Cons of NetSuite Worth ERP
Key Strengths
Unified Cloud Platform
- Single Data Source: NetSuite unifies ERP, CRM, eCommerce, inventory management, and more in one centralised database.
- Real-Time Visibility: Executive dashboards, saved searches, and built-in analytics provide up-to-date insights crucial for effective decision-making in NetSuite’s ERP.
Scalability & Flexibility
- Grows with Your Business: Whether you’re a mid-sized company or a global enterprise, NetSuite can handle increasing transaction volumes and new subsidiaries.
- Customisable: SuiteScript, SuiteFlow, and SuiteBuilder let you tailor workflows, fields, and forms without compromising upgrade compatibility.
Global Capabilities (OneWorld)
- Multi-Currency and Multi-Entity: Ideal for organisations operating in multiple countries or subsidiaries, supporting local taxation rules and language preferences.
- Consolidated Financials: Automated intercompany eliminations, real-time consolidated reports, and local compliance capabilities.
End-to-End Functionality
- Financial Management: A robust set of accounting and financial modules with real-time consolidation.
- Order-to-Cash and Procure-to-Pay: Integrated processes across sales, fulfilment, billing, and procurement.
- CRM and eCommerce: Built-in customer relationship management and online storefront integration.
SaaS Delivery Model
- Reduced IT Burden: No on-premises hardware, plus automatic product updates.
- Predictable Costs: Subscription-based licensing helps convert large capital expenditures into more manageable operating expenses.
Broad Ecosystem and SuiteApps
- App Marketplace: Large ecosystem of third-party integrations for specialised industries or business functions.
- Partner Network: Certified NetSuite Solution Providers and Alliance Partners offer expertise in implementation, customisation, and support.
Limitations to Consider
Cost Structure
- Pricing Complexity: Subscription fees can grow quickly if you need multiple modules, user licenses, or advanced functionality (e.g., OneWorld for multi-subsidiaries).
- Implementation Costs: The initial setup, data migration, and training may be a significant investment particularly for highly customised projects.
Customisation and Resource Needs
- Technical Expertise: While NetSuite provides low-code/no-code capabilities, advanced customisations often require SuiteScript or developer support.
- Time-Consuming Implementations: Complex customisations and integrations can extend go-live timelines without proper planning.
User Interface Learning Curve
- UI/UX: NetSuite’s interface has improved over time, but some users still find it less intuitive compared to modern SaaS solutions.
- Training Required: Ensuring high user adoption may necessitate role-based training and ongoing change management.
Governance and Script Limitations
- Usage Limits: NetSuite enforces “script governance” and API concurrency limits. High-volume transactions or poorly optimised scripts can run into these limits, requiring performance tuning or higher subscription tiers.
- Performance: Very large data sets or high transaction volumes require careful architecture and potentially additional modules or capacity.
Localisation Gaps in Certain Regions
- Tax and Compliance: While NetSuite has strong global capabilities, some countries or regions may lack dedicated localisation bundles. Organisations operating in these areas may need specialised SuiteApps or partner customisations.
- Language Support: NetSuite supports many languages, but some advanced or newly introduced features may lack full translation coverage initially.
Limited On-Premises Options
- Pure Cloud: NetSuite is fully cloud-based, which is typically a strength. However, it can be a limitation for businesses that require on-premises hosting due to strict IT or regulatory requirements.
Real User Feedback of the Netsuite Customer
1. Positive Feedback and Common Pros
Scalability and Growth
- Many users highlight how NetSuite’s modular design and multi-subsidiary capabilities allow them to add users, modules, or even new entities without major system overhauls.
- Companies that experience rapid growth appreciate the cloud-based architecture that can handle increased transaction volumes.
Access to Real-Time Data
- A common praise is NetSuite’s ability to provide real-time dashboards, saved searches, and role-based reports. This helps managers and decision-makers track KPIs and financial data without waiting for manual updates.
- Users also appreciate the unified database; sales, inventory, and financial records sync automatically, reducing data silos.
Cloud Architecture and Automatic Upgrades
- Businesses moving from on-premises solutions often emphasise the convenience of automatic updates and lack of hardware maintenance.
- The SaaS model allows them to focus on core business operations instead of server upkeep.
Overall Impact on Efficiency and Workflow Automation
- Users mention improved order-to-cash and procure-to-pay workflows, especially with NetSuite’s built-in automation features.
- The SuiteFlow tool often gets positive nods for enabling non-technical users to build simple automations.
2. Challenges and Common Cons
Learning Curve
- Numerous users report that the interface and navigation of accounting software like NetSuite can take time to master.
- Training is often necessary, and some organisations find they need a dedicated NetSuite admin or partner assistance, especially early on.
Customisation Complexities
- While NetSuite is highly customisable, some users mention that SuiteScript or advanced configurations can become resource-intensive.
- Large-scale or deeply custom integrations often require experienced developers or a consulting partner.
Cost Structure
- A recurring concern is the subscription-based pricing combined with fees for additional modules or user licenses.
- Organisations with tight budgets or unpredictable user expansion may find costs escalating faster than anticipated.
Performance Issues or Downtime
- A minority of users report occasional performance lags, particularly during peak transactional periods (e.g., month-end, holiday seasons).
- Planned maintenance windows and unexpected downtime can be frustrating for time-sensitive processes, though NetSuite typically schedules maintenance off-peak, ensuring minimal disruption to its user-friendly platform.
3. User Ratings and Review Sources
Summaries from G2 and Capterra
- G2: NetSuite often scores highly (in the 4.0–4.3 range out of 5) for functionality, breadth of features, and scalability in user reviews. Users who fully adopt the platform’s modules generally rate it favourably.
- Capterra: Common praises include robust ERP capabilities and integrations, while critiques centre on cost and learning curve. Overall ratings tend to sit around 4.0 to 4.2 stars.
Other Popular Review Platforms
- TrustRadius: NetSuite is often commended for its “all-in-one” approach. Users appreciate that they can manage finances, CRM, eCommerce, and more without juggling multiple systems.
- Software Advice: Similar to G2 and Capterra, reviews emphasise strong functionality but note that smaller or very specialised businesses may find licensing costs steep.
Specific Examples or Quotes from Business Owners or Administrators
- “Finally getting all of our inventory & finances under one platform has been nice, and the ability to create custom saved searches and financial statements. I handle all of the AP as well and this has been a much better process than just entering a bill in Quickbooks.” – Chris T. – Bookkeeper
- “NetSuite stands out amongst the competition with its comprehensive and scalable cloud based solution, which specialises in business operations across all key business areas. NetSuite has allowed our business to eliminate disparate systems and reduce our overall tech stack by integrating financials, inventory management and procurement into one global solution.” – Clay L.-Director of IT
- “Overall quite positive. The program features have allowed us to track our inventory in ways we couldn’t do with QuickBooks and except for the reporting issues the program has been quite intuitive.” – Garth T.- Dir. Accounting and Finance
Suitability for Different Business Sizes and Industries Experience
1. Small and Midsize Businesses (SMBs) for Customer Support
Modular Approach and Scalability for Growing Businesses
- Start Small, Expand Gradually: SMBs can begin with core financials (e.g., General Ledger, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable) and then activate additional modules (like CRM, Inventory, and eCommerce) as they grow.
- Cloud Delivery: Because NetSuite is cloud-based, SMBs don’t need extensive IT resources or expensive on-premises hardware.
- SuiteSuccess Methodology: NetSuite provides industry-specific starter packages with preconfigured roles, workflows, and dashboards. This reduces the complexity of adopting advanced modules down the road.
Typical Implementation Timelines and ROI
- Implementation Time Frame: SMB implementations can often be shorter, ranging from a few weeks to a few months, depending on complexity and data migration needs.
- Faster Time to Value: By consolidating data into one system, SMBs typically see improvements in cash flow visibility, inventory accuracy, and order processing speed.
- Scalable for Expansion: As SMBs grow (new products, acquisitions, or multiple business units), NetSuite’s flexible architecture allows them to add users, subsidiaries, and advanced modules without re-platforming.
2. Large Enterprises
Enterprise-Grade Functionality, Multi-Entity Support, and Global Capabilities
- NetSuite OneWorld: Large, multinational enterprises benefit from OneWorld features, handling multi-currency, multi-language, and multi-subsidiary structures in a single account.
- Global Consolidations: Automated intercompany transactions and real-time financial consolidation streamline reporting across numerous entities or regions.
- Compliance and Regulatory Support: Built-in tax engines, e-invoicing capabilities, and country-specific localisations help enterprises remain compliant worldwide while using NetSuite’s accounting features.
Custom Configurations for Complex Operational Structures
- Advanced Modules: Larger enterprises may deploy specialised modules like Advanced Revenue Management, Demand Planning, Supply Chain Management, or SuiteProjects (PSA).
- Extensive Customisation: NetSuite’s SuiteScript and SuiteFlow enable deep customisation for unique processes, while RESTlets and SuiteTalk connect NetSuite to external applications (e.g., custom logistics, HR solutions).
- Sandbox and Development Tools: Enterprises with complex or mission-critical processes can use Sandbox environments and the SuiteCloud Development Framework (SDF) for continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) best practices.
3. Industry-Specific Customisations
Vertical Solutions (e.g., Retail, Manufacturing, Nonprofit, Software)
- Retail and eCommerce: NetSuite offers SuiteCommerce, a built-in eCommerce platform with inventory and order management integrations. Retailers benefit from omnichannel capabilities, real-time inventory tracking, and customer-centric analytics.
- Manufacturing and Distribution: Modules for MRP (Material Requirements Planning), warehouse management, and demand planning allow manufacturers to optimise production schedules and supply chain operations.
- Nonprofit and Charitable Organisations: Nonprofit vertical solutions provide grant management, fund accounting, and donation tracking.
- Software and SaaS Companies: NetSuite offers subscription billing, revenue recognition, and automated renewals tailored to recurring revenue business models.
Importance of Specialised Modules and Partner-Built SuiteApps
- Partner Ecosystem: A rich SuiteApp marketplace offers third-party solutions for niche needs, such as advanced budgeting/forecasting tools, specific tax compliance for certain countries, or industry-specialised integrations.
- Vertical Best Practices: Partners and NetSuite’s own SuiteSuccess editions come with preconfigured dashboards, workflows, and reports aligned to common industry requirements.
- Customisation vs. Configuration: While many needs can be met through NetSuite’s out-of-the-box industry solutions, specialised SuiteApps can further extend functionality without sacrificing maintainability or upgrade safety.
Comparison to Other ERP Solutions
1. Top Competitors
SAP
- Overview: SAP offers a wide range of ERP solutions, while NetSuite is a leading accounting software solution for large enterprises and mid-market organisations.
- Market Position: Dominant among Fortune 500 companies, especially those with complex manufacturing or supply chain operations, NetSuite’s ERP is often the go-to choice.
- Target Audience: Enterprises with intricate global processes, multi-plant manufacturing, and extensive reporting needs.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Overview: Microsoft’s ERP portfolio includes Dynamics 365 Business Central (for SMBs) and Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain Management (for mid-market to large enterprises).
- Market Position: Strong presence in companies already using the Microsoft ecosystem (e.g., Office 365, Azure) and those wanting more flexible deployment (cloud or on-premises).
- Target Audience: Organisations seeking tight integration with Microsoft products with moderate to complex requirements.
Oracle ERP Cloud
- Overview: Oracle’s flagship cloud ERP targets large enterprises or rapidly growing mid-market companies needing advanced financials, procurement, and enterprise performance management.
- Market Position: Competes with SAP in the large enterprise space, offering deep functionality for finance-heavy or multi-entity organisations.
- Target Audience: Global corporations with complex legal structures, as well as existing Oracle databases or on-premise ERP customers migrating to the cloud.
Other Mid-Market Solutions
- Infor, Epicor, Acumatica, SYSPRO: Each cater to specific niches, e.g., Infor in manufacturing/distribution, Epicor for mid-market manufacturers, and Acumatica for cloud-first, flexible deployments.
2. Key Differentiators of NetSuite
Cloud-First Architecture
- Pure SaaS: NetSuite was built in the cloud from day one, unlike many competitors that originated on-premise and later transitioned to the cloud, making it a preferred choice for businesses looking to go with NetSuite.
- Automatic Updates: Users receive new features and patches without on-premise upgrade projects.
Built-In CRM
- Single Data Model: NetSuite unifies ERP with CRM, eCommerce, and professional services automation (PSA) on a single platform, reducing the need for separate systems or heavy integrations in business management software.
- End-to-End Visibility: Sales, support, and financial data all live in the same database, enabling real-time insights across departments.
Scalability and Multi-Subsidiary Support
- NetSuite OneWorld: Handles multi-currency, multi-language, and multi-entity structures for global businesses.
- Highly Configurable: From SMBs to multinational enterprises, NetSuite’s modular design can accommodate evolving needs.
Third-Party Ecosystem and Integration
- SuiteApp Marketplace: A robust ecosystem of partner-built applications that extend NetSuite’s capabilities (e.g., specialised tax engines, advanced WMS, etc.).
- APIs and Connectors: SuiteTalk (SOAP/REST), RESTlets, and integrations with popular iPaaS providers (Celigo, Dell Boomi, MuleSoft) ensure that NetSuite can connect to almost any external system.
3. Where NetSuite Shines / Where It May Lag
Where NetSuite Shines
Mid-Market and Growing Companies
- Ideal for businesses outgrowing entry-level systems (like QuickBooks) that need robust financials, inventory management, or global consolidation but don’t want the overhead of a heavy, on-premise ERP.
- Fast-growing startups in software, eCommerce, or services appreciate the modular approach and built-in CRM.
Global Operations
- OneWorld provides real-time consolidation, multi-currency management, and local tax compliance. This is especially strong for companies with multiple legal entities and cross-border transactions.
Unified Platform
- The ability to manage financials, CRM, eCommerce, and professional services automation in one system is a major advantage for organisations seeking an all-in-one solution.
Quick Implementation for Standard Use Cases
- SuiteSuccess industry editions offer preconfigured roles, dashboards, and workflows that can shorten the time to go-live (especially for typical scenarios in retail, distribution, services, etc.).
Where It May Lag
Highly Complex or Customised Manufacturing
- Deep, specialised manufacturing environments (e.g., aerospace, automotive, process manufacturing) may prefer SAP or Infor due to richer native MRP, BOM, or plant floor control capabilities though NetSuite’s ecosystem is improving in this area.
On-Premise Requirements
- NetSuite is exclusively cloud. Organisations requiring an on-premise or private cloud deployment for regulatory or internal IT reasons cannot deploy NetSuite outside of Oracle’s data centres.
Cost Structure and Licensing
- Some businesses find NetSuite’s subscription and add-on module pricing can climb quickly if they require many advanced features. Competitors like Acumatica or Microsoft Dynamics 365 might offer more flexible scaling in certain scenarios.
User Interface and Learning Curve
- While the UI continues to evolve, some users find NetSuite’s interface and navigation less modern compared to newer cloud-only solutions. Adequate training is crucial for ensuring user adoption.
Implementation Best Practices
1. Planning and Readiness
Assessing Business Needs and Process Mapping Before Deployment
- Requirement Gathering: Conduct thorough interviews with key stakeholders (finance, operations, sales, IT, etc.) to understand their workflows, pain points, and ultimate goals.
- Process Mapping: Document current processes (order-to-cash, procure-to-pay, monthly close) and note where improvements or automation are desired. This will guide how you configure NetSuite modules, forms, and workflows.
- Software Fit: Compare these needs to NetSuite’s out-of-the-box functionality. If gaps exist, plan for custom fields, SuiteScripts, or third-party integrations (SuiteApps).
Setting Clear Goals and KPIs for Success
- Define Measurable Objectives: Identify metrics like reduced month-end close time, higher inventory accuracy, or fewer manual data entries.
- Timeline and Milestones: Establish a realistic project timeline with clear deliverables (e.g., completion of data migration by X date, user acceptance testing by Y date) to ensure a smooth experience with NetSuite.
- Continuous Improvement: Recognise that post-launch optimisation will be ongoing. Defining initial KPIs sets a baseline to measure continuous enhancements.
2. Team and Stakeholder Engagement
Importance of Executive Sponsorship and User Training
- Executive Buy-In: An executive sponsor (C-level or director) can champion the project, allocate resources, and help align cross-departmental cooperation, which is crucial for the successful implementation of a powerful ERP.
- Change Management: ERP implementations impact many roles. Early, clear communication about the benefits and impacts of using NetSuite reduces resistance and smooths adoption.
- Role-Based Training: Develop targeted training for end users, power users, and administrators. Employees who understand the “why” behind NetSuite’s processes are more likely to embrace the system.
Ongoing Support and Documentation
- Formal Support Mechanisms: Decide if you’ll rely on NetSuite’s support tiers or partner support. Some organisations choose a hybrid approach with both in-house NetSuite admins and partner expertise.
- Training Materials: Provide easy-to-access resources (knowledge base articles, recorded webinars, step-by-step guides). Update them as processes evolve.
- Feedback Loops: Encourage user feedback via surveys or regular check-ins. This helps identify areas needing refinement, additional training, or enhancements.
3. Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Underestimating Customisation Needs or Data Migration Complexity
- Customisation Scope Creep: Often, businesses initially assume they’ll only need standard functionality. In reality, specialised workflows or advanced modules (e.g., revenue recognition, multi-subsidiary, WMS) may be essential. Anticipate potential customisation early.
- Data Cleanup and Migration: Migrating dirty or duplicate data leads to inaccurate transactions and reporting post-go-live. Assign time and budget to cleanse data, map legacy fields to NetSuite, and conduct multiple trial runs before final cutover.
Not Planning for Post-Launch Support and Adoption Challenges
- Post-Go-Live Hypercare: In the first weeks after deployment, you’ll likely see a spike in support tickets and user questions. Plan extra resources to address these quickly.
- User Adoption: Even with training, employees may revert to old systems or spreadsheets if NetSuite tasks aren’t intuitive. Continuous reinforcement, refresher training, and refining the user interface can boost adoption.
- Future Enhancements: NetSuite is robust, regularly updated, and receives positive reviews from users. If you don’t plan for ongoing improvements and training on new features, your system can become underutilised. Maintain a roadmap of future enhancements tied to business goals.
Conclusion

NetSuite’s Business Intelligence and Reporting capabilities stand out as a seamless, integrated solution designed to provide real-time, data-driven insights. By centralising key business information covering finance, operations, sales, inventory, and more, NetSuite enables users at every level of the organisation to uncover valuable trends, perform detailed analyses, and make evidence-based decisions. Tools like SuiteAnalytics, Saved Searches, and Workbooks empower both technical and non-technical stakeholders to generate reports, set KPIs, and explore data through customisable dashboards, significantly reducing reliance on external applications or IT support.
Furthermore, the flexibility to integrate third-party BI tools and the ability to pull data via SuiteAnalytics Connect provides even more advanced analytics possibilities. Whether a company opts to stay entirely within NetSuite or to merge its NetSuite data with other enterprise systems, the platform’s open architecture ensures smooth interoperability. Combined with robust security protocols, role-based permissions, and audit trails, NetSuite’s reporting environment delivers both the transparency and governance that modern businesses demand.
Ultimately, by uniting powerful analytics tools with an intuitive user experience, NetSuite’s BI and reporting framework helps organisations elevate their strategic planning, optimise day-to-day operations, and adapt swiftly to evolving market conditions, all while maintaining a unified system of record and strong compliance controls.

