In an era where organisations grapple with volumes of data originating from sales, finance, and beyond, the urgency to harness analytics in a more data-driven way has never been greater. Recent industry statistics suggest that over 90% of organisations achieved measurable value from data and analytics investments in 2023. Yet many still struggle with overload and underutilised insights. Below is a comprehensive exploration of how embedded analytics can transform your ERP system, streamline your business process, and bolster decision-making across every department.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Understanding Data Overload in ERP Systems
- 3 What Is Embedded Analytics in ERP?
- 4 Benefits of Embedded Analytics for Modern ERP
- 5 Integration Strategies: Transforming ERP with Data Insights
- 6 Embedded Analytics Features That Drive Success
- 7 Use Cases: Real-World Scenarios of Embedded Analytics in ERP
- 8 Action Steps: Implementing an Embedded Analytics Platform
- 9 Best Practices for Data-Driven Decision-Making in ERP
- 10 Conclusion
Introduction
In enterprise resource planning, executives frequently encounter a monumental challenge: managing an ever-increasing influx of data. Traditional reporting methods often fail to keep pace, leaving leadership teams hungry for real insights. The good news? Analytics in ERP has evolved far beyond the days of clunky spreadsheets and siloed BI platforms. Instead, embedded analytics is part of a new paradigm that integrates analytics directly into their ERP applications so business users can effortlessly analyse data.
Key Insight: As modern industries rely on agile workflow and integration with external systems, real-time analytics fosters faster decision-making and deeper analytical understanding across operations.
This article will illustrate how analytics nested within the ERP software empowers executives to glean robust, data-driven insights, minimise blind spots, and optimise critical processes like supply chain, sales, and financial management.
Understanding Data Overload in ERP Systems
1: The Challenge of High Data Volumes
The sheer magnitude of operational data generated every day can be staggering. According to a 2023 survey by a global consultancy, the average organisation processes hundreds of gigabytes or even terabytes of data weekly. Without the right analytics tools, crucial intelligence slips through the cracks.
- Fact: Many industries, including retail and manufacturing, have seen a 45% uptick in data generation in the last two years.
- Impact: Delayed analytics initiatives and poorly structured data lead to inefficiencies in business process flows.
2: How Data Overload Impacts Business Process
Legacy ERP systems might not offer advanced analytics capabilities out of the box. When an organisation tries using ERP that lacks robust analytics functionality, critical patterns or anomalies remain hidden, impeding the entire workflow.
- Result: Missed opportunities in cost reduction, process optimisation, and customer satisfaction gains.
- Consequence: Decision-makers struggle to generate timely insight, ultimately hindering the potential of the ERP system.
3: Transition to Data-Driven ERP
Companies looking to become truly data-driven increasingly turn to real-time analytics and visualisation. This means a move to a cloud-based ERP model or hybrid approach, reinforcing an interconnected ecosystem.
- Opportunity: Upgrading to a new ERP with a built-in analytics platform ensures quicker results and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
- Trend: Many enterprises now integrate a data warehouse for more efficient data retrieval, ensuring that ERP data remains accessible and secure.
What Is Embedded Analytics in ERP?

1: Definition and Core Concepts
Embedded analytics is the seamless weaving of analytics directly inside ERP applications, providing real-time dashboards and data without requiring teams to toggle between separate software applications.
- Difference from Standalone BI: External BI software solutions require more steps, which frequently cause slowdowns. In contrast, embedded analytics are nestled within the interface workers already use, causing little disruption to daily business operations.
2: How Embedded Analytics Can Help
Embedded analytics can help organisations keep pace with the demands of a digital-first marketplace. Because employees no longer need a separate login for analysis, they gain immediate situational awareness and can swiftly manage anomalies.
- Example: SAP Embedded Analytics uses a strong analytics solution that integrates financials, HR, and logistics data into a central system, doing away with guesswork.
- Data Visualisation: The intuitiveness of chart and analytics user interfaces enables trend and outlier spotters while accelerating response times.
3: The Role of Self-Service Analytics
Self-service is crucial, particularly for busy executives and managers. It empowers them to craft custom reports, run data analyses, and glean an insight or two without waiting on IT support.
- Outcome: Greater organisational agility, wherein executives can act on changing market conditions within minutes.
- Approach: Self-service analytics fosters a culture of curiosity and proactive problem-solving.
Benefits of Embedded Analytics for Modern ERP
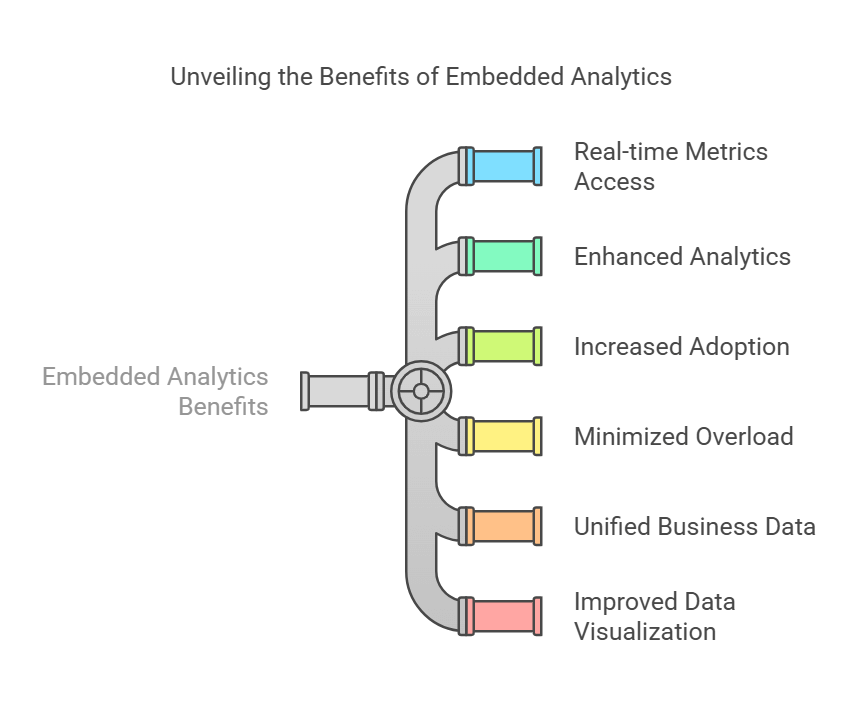
1: Streamlined Real-Time Data Analytics
- Access real-time metrics within the ERP system interface. Spot sales dip the moment they happen.
- Enhanced analytics shortens the feedback loop, reducing the lag between data capture and decision-making.
2: Increased Adoption and Reduced Overload
- When teams don’t have to switch platforms, they’re more likely to embrace embedded analytics wholeheartedly. Adoption rates spike.
- Minimise informational overload by consolidating relevant insights into a single dashboard or tab.
3: Enhanced Business Intelligence and Reporting
- Robust analytics unify business data from departments like finance, inventory, and supply chain management, leading to sharper business intelligence.
- Real-time charting, data visualisation, and interactive queries deliver a more analytical perspective, turning dense datasets into accessible knowledge.
According to a 2022 study, more than 70% of SMES are willing to purchase a cloud solution next time they need a new application.
Integration Strategies: Transforming ERP with Data Insights
1: Cloud & Hybrid Integration
Many organisations implement software as a service or hybrid environments to ensure maximum scalability. A data warehouse can feed on-premise, cloud-based ERP, and external data points to unify everything in real time.
- Recommendation: Evaluate different ERP solutions to determine their ability to handle your existing or future data warehouse and adapt as your firm grows.
2: Use of Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Augmenting embedded analytics features with artificial intelligence can be game-changing. Predictive analytics harnessess historical data to forecast operations, finances, or customer behaviour trends.
- Impact of ERP: You will be able to proactively act on stockouts or even a surge in demand with AI algorithms plugged into ERP-embedded analytics.
- Outcome: A more resilient supply chain anchored by data-derived predictions.
3: Ensuring Secure Data Flow
To maintain trust, guarantee compliance with regulations like GDPR. ERP systems are designed to incorporate built-in encryption and access controls. Still, confirming your chosen integration approach preserves data integrity at every juncture is essential.
- Confidence: A well-secured environment fosters user trust, mainly when executives rely on sensitive operational data for strategic moves.
Embedded Analytics Features That Drive Success
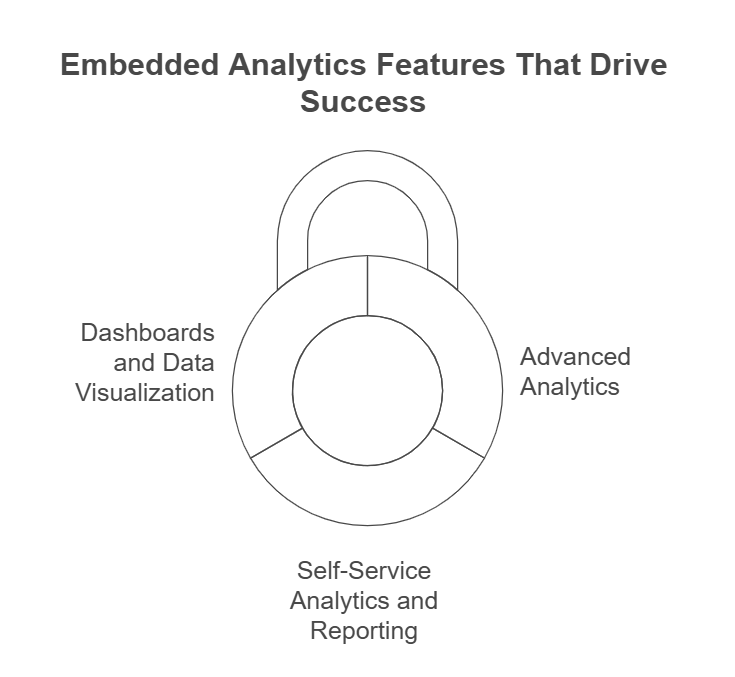
1: Dashboards and Data Visualisation
A nice-looking dashboard can de-mystify complex data relationships. Charts, graphs, and pivot tables enable teams to spot high-level or granular trends quickly.
- Tip: Effective data modelling harmonises disparate datasets, feeding coherent analytics into user-friendly visualisation layers.
- Note: Analytics makes high-level metrics easier to digest, empowering staff to act immediately.
2: Self-Service Analytics and Reporting
Self-service analytics is vital for teams that need immediate answers. When embedded analytics is part of the daily workflow, employees feel empowered rather than restricted.
- Workflow Integration: Users can generate real-time analytics and reporting without leaving the ERP functions environment. This streamlines daily tasks.
- Efficiency: Freed from IT bottlenecks, managers can respond to dynamic market shifts by pulling custom reports at will.
3: Advanced Analytics Capabilities
Cutting-edge analytics tools, sometimes called embedded BI, go beyond static dashboards. They incorporate correlation matrices, anomaly detection, and advanced scenario planning.
- Analytics solutions often include performance triggers that alert stakeholders to changes.
- Example: Analytics directly inside your ERP might highlight sudden spikes in returned merchandise, prompting an immediate remedial strategy.
Use Cases: Real-World Scenarios of Embedded Analytics in ERP
1: Financial Planning & Reporting
Analytics can evaluate multi-year financial projections, revenue breakdowns, and cost overviews. When integrated with data from multiple finance modules, CFOs can see a consolidated budget snapshot.
- Result: Swift pivots in resource allocation.
- Outcome: More accurate forecasting and better investor relations.
2: Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, embedded analytics reveals bottlenecks in shipping routes or production lines. Imagine automatically triggering reorder points when certain thresholds are met.
- Real-Time: Updated information ensures faster reaction to vendor issues or changing customer demand.
- Key ERP advantage: Using a single ERP system to track everything from procurement to shipping fosters synergy.
3: SAP Embedded Analytics for Large Enterprises
SAP Embedded Analytics exemplifies how a robust business intelligence software solution can unify data streams across multinational corporations.
- Highlight: Because it integrates seamlessly, executives see operational updates in near real-time, leading to quicker, more informed decisions.
- Direct Benefit: Unified viewpoint of localised warehouses, inventory levels, and financial health across multiple continents.
4: Tracking Key ERP Metrics
Organisations often measure on-time deliveries, lead conversion, or production throughput as part of their success with ERP deployments.
- Embedded Analytics advantage: Track all metrics within the ERP to ensure consistency, accuracy, and immediate feedback loops.
Action Steps: Implementing an Embedded Analytics Platform
1: Identify Your Objectives and Use Cases
- Strategy: Clarify your target outcomes. Are you focused on cost efficiency, revenue growth, or operational agility?
- Checklist: Investigate the types of ERP your organisation currently runs and whether you need a new ERP to support an analytics platform seamlessly.
2: Choose the Right Analytics Solution
- Analytics solution: Determine if you’ll rely on a native module from ERP providers or integrate a third-party tool.
- Factors: Assess user interface, real-time data refresh rates, and alignment with your existing management software.
3: Incorporate Self-Service and Visualisation
- Execution: Roll out dashboards and data visualisations that adapt to various departmental needs, from finance to HR.
- Training: Provide tutorials on generating custom reports. A well-prepared staff unlocks the full power of data and analytics.
4: Test, Measure, Iterate
- Continuous Improvement: Gather feedback on what’s working or not.
- Manage: Update security protocols regularly to protect sensitive information, ensuring your integration is dynamic and safe.
Best Practices for Data-Driven Decision-Making in ERP
1: Foster a Data Culture
Leadership must promote a mindset where employees rely on factual evidence rather than intuition alone. Analytics enables more precise interventions, from marketing campaigns to resource allocation.
- Result: A self-sustaining environment of constant improvement.
2: Streamlined Data Governance
Ensuring controls, naming conventions, and validation will ensure that data is clean, consistent, and actionable. ERP systems have built-in checks for data integrity, but corporate policies should comply.
- Added Benefit: Minimises confusion and ensures that every stakeholder references the same set of truths.
3: Leverage Predictive Insights for Competitive Advantage
When you embed predictive analytics; coupled with AI – into your daily operations, your organisation moves from reacting to anticipating market shifts.
- Real-Time Data: It combines historical patterns with current signals to let you respond ahead of the competition to micro-trends.
- Analytics provides a crucial edge: smarter scenario planning for product launches, expansions, or cost-saving measures.
Conclusion

Embedded analytics in an ERP system revolutionise how organisations harness volumes of data for sharper, more analytical results. Integrating analytics directly and offering self-service capabilities amplifies efficiency, collaboration, and oversight, ultimately driving long-term value creation.
Final Note: By adopting these practices and embracing an analytics-driven future, you set the stage for sustained growth, deeper market penetration, and a thriving business intelligence culture. Whether you’re evaluating SAP Analytics Cloud or another software that organisations use, remember that success hinges on actionable insights gleaned from the ERP software.


