The theory of triple constraints in project management is easy to understand. Triple constraints theory says that any project works within the boundaries of scope, time, and cost. Changes in any one aspect lead to changes in the other two.
There is a need to strike a proper balance of all these variables to ensure the desired results. These variables are there with us throughout the project. For any project to succeed, it is of utmost importance to gain proper equilibrium between time, scope, and cost.
For example, changes in the project’s budget (cost), whether shrinking or increasing the cost, directly impact the scope and time required to complete the project.
It is the job of the project manager to ensure proper trade-offs between these triple constraints. One also manages and monitors all the resources needed for the project’s completion. It is his responsibility to make all the people working on the project understand their work.

Contents
The Golden Triangle
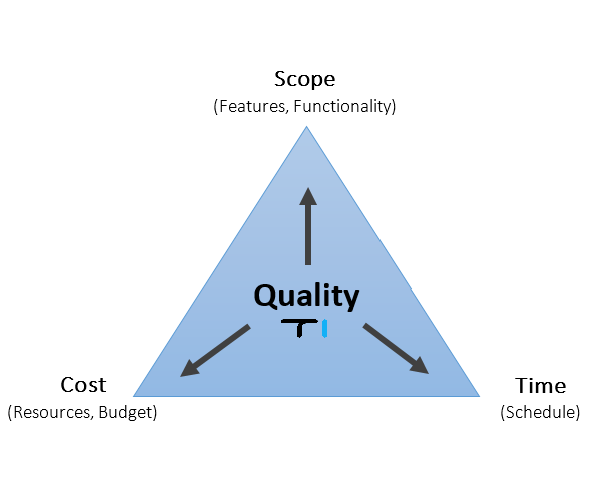
The Golden Triangle is also known as the Iron Triangle, the triple constraints of project management, or the project management triangle. In a triangle-like structure, each vertice represents time, cost, and scope, respectively. The Quality dominates the centre of the triangle.
All these factors in the Golden triangle are interrelated and interconnected to each other. Any changes in any one constraint will directly affect the Quality of the work done.
There are three basic key constraints that are interlinked to each other. These are the critical elements required to ensure the final results of the project.
The project manager has to juggle between these three elements and ensure the best combination of the variables. It does not imply that other aspects, such as human resources, risk management, procurement management, resource allocation, etc., are not crucial for the project.
The central theme of the project revolves between these ideas:
- The completion of the project should be before or on the due date estimated.
- The cost of the project shouldn’t cross the estimated budget.
- The scope of the project should achieve and meet all the consumer’s expectations.
- The customer should be satisfied with the Quality of the project.
The triple constraints theory contains 3 variables, namely:
- Time
- Cost
- Scope
Let’s study these variables in detail.
Time
The given project should be completed and delivered on time. All the activities related to the project should be planned and scheduled accordingly to ensure timely completion of the project.
The time required for the completion of a project should be calculated efficiently. Every project has a deadline, and these deadlines should be realistic.
If the scope of the project broadens, then the time required for completion will increase. This will eventually lead to an increase in the cost of the project. If you want to complete the project in less time, you will need more resources and trimming of your scope.
Hence, a proper balance between these elements is necessary. Proper planning and scheduling of tasks are essential to meet the timeline of the project.
It is essential to allocate a fixed time and schedule to a particular task. It will also help the team members clearly understand the requirements of the work and their deadlines. Proper scheduling will enhance the Quality of the project.
The methods used to estimate the time required are the PERT chart, critical path method, top-down or bottom-up approach.
PERT chart
Program Evaluation Review Technique helps to break individual tasks of each project and better analyze them. This project management tool then provides a graphical representation of the project for better understanding.
Critical path method
CPM is an algorithm that helps to identify the longest task sequence duration for completing a project. It identifies all the crucial activities and deadlines which should be completed on time.
Top-down approach
This approach begins with defining the objective and listing the tasks involved in the project. Then these tasks are further classified and assigned to the team members. This approach works when the objectives are defined clearly.
Bottom-up approach
This approach refers to first brainstorming all the activities required to finish the project. After the tasks are defined, then you should organize the tasks into specific groups. Though this approach is a bit time-consuming, it ensures detailed scheduling.
These tools will ensure a systematic planning of the activities and automated calculation of the time required to complete a project successfully. It will help to calculate the realistic timing needed to complete a task.
Cost
Cost refers to the amount needed to complete a project. Estimating the money required for the project is of utmost importance. A considerable amount of cost is allocated for the resources, assets, and labour that will be required to complete a project successfully.
Cost is incurred to acquire the resources of the project. If you want good and experienced people to work on your project, you will need to pay good money. Similarly, for the good Quality of work in your project, you have to invest money and acquire quality assets and resources.
For the project to meet its final objective, it is necessary to allocate an efficient budget for all the related activities. From the smallest costs like electricity bills to huge costs such as buying machinery, all the costs should be calculated according to their actual price.
Calculation of all the costs is essential to ensure that the project is not under budget or over budget. The under budget project may give poor quality results as the resources used for the projects are poor. And the over-budget projects often waste resources by not using them to their full potential.
So, before allocating the budget, it is crucial to calculate each of the individual costs. Then add all the individual costs to get the overall project costs.
Costs are segregated into two:
- Recurring costs
- Non-recurring costs
Recurring costs
It refers to those costs which are required to operate a project. These operating costs are incurred at a regular interval of time and are usually fixed. Some recurring costs for a project are the workers’ salary, rent for the place, electricity and telephone bills, etc.
Non-recurring costs
These costs are very unpredictable and can happen at any interval of time. These costs are capital expenses that are usually one-time. They are unlikely to occur frequently in the future. Examples of non-recurring costs are buying an asset, infrastructural costs, buying land, etc.
Every aspect of the project has a due cost. Negotiating the anticipated costs of any activity will lead to a compromise in the Quality of the project. And if the Quality of the project is compromised, it will lead to unsatisfied customers.
It is the duty of the project manager to estimate the costs and allocate them responsibly. One should monitor the budget and efficiently handle any excess costs while working on a project. If the cost is high, then consult your client and explain the situation intelligently.
Scope
The scope is the requirements and objectives of the project that are to be fulfilled. The scope of the project is defined at the starting or initial phase of the project. The customer tells his requirements about the project, which then becomes the base of the project. According to this base, then information regarding similar projects, historical data, and statistics are acquired.
The scope also helps to decide all the work to be done to complete the project successfully. It forms the project’s foundation, which helps schedule the time and estimate costs associated with the project.
The scope forms the base on which other elements related to the project are decided. For a project to succeed, it is necessary to do dept research and accurately plan the scope. The more accurate and well defined the scope, the more it will help the project to meet its objectives and succeed.
The scope of the project directly impacts Quality and output. Any alteration between the project’s working will lead to compressed time schedules, resulting in inflated costs.
Starting the project with an unclear scope will result in the undesirable and unexpected outcome of the project. So, defining the scope of the project is very crucial for everyone.
The scope is defined to get the desired output after the project’s completion. The scope is the time required to complete the project and the resources associated with the project. For a project to be successful, it is of vital importance to meet the objectives of scope.
The project manager should act according to the defined scope to achieve the objectives. The goals and objectives of the project are met only after meeting or exceeding the project scope.
If the project scope is not achieved, it means that the customer’s demands are not fulfilled. And this will eventually lead to a dissatisfied customer.
The project manager must properly monitor and meet the expectations of the project. It sometimes happens that you are halfway done through the project, and there are some changes or additions to the project’s scope. These alterations can come from your client, co-worker, or customer.
This sudden change or addition to the whole or part of the project is known as scope creep. These alterations of the project will ultimately lead to extended delivery time and costs. This phenomenon can happen several times in the life of a project.
To better tackle this situation, it is better to be prepared in advance and accept the decision. You should notify all the stakeholders about this new change and inform the customer about the late delivery.
These were the three constraints of project management. But there is another constraint that is connected and affected by these three constraints. That constraint is called Quality.
Now, let’s study Quality in detail.
Quality
The quality variable is the central focus of the three constraints. All the cost, time, and scope variables are on the vertices of the triangle. And the quality constraint takes the central place in the triangle.
This eventually points out that Quality is the end output of any project. The cost, time, and scope constraints help to enhance the Quality of the project. Quality is the end result of every project. It will either satisfy or dissatisfy the customers.
Better Quality of a project is the project which meets the requirements and objectives of the customer. Good quality projects are often planned according to the project’s scope and require less reworks.
When a project meets the projects’ scope within the boundaries of allocated time and costs, the project’s Quality is maintained. This type of quality project fulfils all the specifications and requirements of the project and ensures a long-lasting impact on the customer.
The Quality of the project should be maintained regularly. You should monitor and control the project’s Quality from the start to the end of the project. Poor Quality of work would lead to outcomes that are not long-lasting and durable.
It is rightly said that people forget how quickly you completed the job, but they remember how well you did the work. So, never compromise on the Quality of your work.
For example, you are required to construct a bridge within 20 days, and with 3 million dollars. Now, you know you will need at least 5 million dollars to construct a durable, good quality bridge. But you are only given 3 million dollars, and you build the bridge with low-quality resources.
And on the day of the inauguration, the bridge collapses. This is because the low-quality resources are not able to handle the pressure. This would bring embarrassment to the sponsors, builders, and team members who helped build the bridge.
If the Quality of the project is compromised, all the costs and time are wasted. So always have the target of getting quality work done and make your client understand the same.
Understand the interconnection between the constraints
The triple constraints often influence one another, and alterations in any one of the constraints will lead to changes in the other two. All these variations in the project will ultimately affect the Quality of work done.
Here, one variable depends on the other, and changes in any would lead to intense monitoring and controlling of the project to achieve the project’s requirements.
Let us consider an example to understand this interrelation:
You are a builder, and your sponsor has asked you to build 1 row-house. Here, you will need 1 year and 1 million dollars to complete this project.
So,
- Scope- to construct 1 row-house
- Time required- 1 year
- Cost associated- 1 million dollar
Scenario 1:
Here, the sponsor wants to build 5 row-houses. Then the time required to finish this project will become 5 years, and the cost will change to 5 million dollars.
The changes would be as follows:
- Scope- to construct 5 row-houses.
- Time required– 5 years
- Cost associated- 5 million dollars
Scenario 2:
Now, the sponsor wants the cost to be 3 million dollars. Then the scope will then change to constructing 3 row-houses, and it will require 3 years for the completion.
The alterations made would be:
- Cost associated- 3 million dollar
- Scope- to construct 3 row-houses
- Time required- 3 years
Scenario 3:
The sponsorer wants to complete this project in 2 years. Now, the scope would change to the construction of 2 row-houses. Similarly, the cost needed to complete the project would be 2 million dollars.
Following would be the changes:
- Time required- 2 year
- Scope- to construct 2 row-houses
- Cost associated- 2 million dollar
Note: The example is a work of fiction and does not imply any connections to reality. It helps in better understanding the concept.
As you can see, change in any constraints scope (scenario 1), cost (scenario 2), or time (scenario 3) will ultimately affect other constraints of the project. We can conclude by saying 1 factor leads to changes in the other 2 factors and vice-versa.
Why is managing the triple constraints of the project important?
These triple constraints have a give and take relationship. They are changing and adjusting to each other constantly. It is of utmost importance to manage this golden triangle efficiently.
Some of the importance of triple constraints are as follows:
- Change Management
Triple constraints help us to be prepared for any unforeseen changes in the project. In the life of the project, it is bound to be amended many times. And every time, you have to begin from the start. Triple constraints help us in properly understanding the scope. And any changes in the scope would directly affect the time and cost of the project. It is easier to manage changes if the project manager knows about the iron triangle and its impact. It will eventually assist us to adjust to the changes by better monitoring and controlling the project.
- Timely delivery of the project
The project manager is responsible for planning and estimating the costs of the project. Assume everything is going smoothly and the project is almost done. Suddenly there are changes made to the scope of the project. Now the project will require more time for completion.
Here, if the project manager is experienced and has knowledge about the golden triangle, one would handle changes effectively and manage all the resources. This will ensure the timely completion of the project.
- Better performance
The iron triangle helps the project manager to become proactive and flexible. It helps to keep the project on track with the expectations of the customer. It provides the base through which Time, Costs, Quality, and other variables are measured.
It assists us to change with the changing requirements and still helps in delivering quality output on time. The triple constraints help in promoting transparency and accountability to all the stakeholders in the project. All this leads to the dynamic performance of the project.
- Face the obstacles in the way
As we have seen before, this triangle helps us to combat changes and adjust situations according to changing environments. This also involves foreseeing obstacles that could come in the way and prevent the project’s smooth working.
This triangle would help the project manager to identify the obstacles. It suggests remedies to ensure smooth and timely delivery of the project. For the project to work efficiently, lesser surprises are better. The Quality of the project will be maintained if the obstacles and changes are overcome successfully.
- Achieve the scope of the project
The requirements and needs of the project are known in the initial phase of planning the project. These requirements form the basis through which a task is identified and assigned. The triangle systematically represents the scope based on which time and costs are estimated. This proves to be beneficial and helps reduce scope creep.
All these factors eventually help the project to meet the end requirements of the scope. It also helps to better access, manage and monitor the progress of the project.
How to use the triple constraint effectively?
It is essential to balance all the constraints of the project as they are interdependent. A project manager should efficiently manage the variables. A change in the balance of the variables would lead to a sudden increase in the costs, unclear scope, and delayed delivery time.
To avoid this, the project manager should smartly use the triple constraint theory to satisfy the customer and successfully achieve the project’s requirements.
Some tips that can help use triple constraints effectively are as follows:
- Clearly understand the three constraints and align them to set expectations.
- Clearly define and understand the scope of the project
- Communicate the scope openly to all the stakeholders.
- Monitor and review the work is done regularly and ensure meeting the deadlines.
- Evaluate changes and offer solutions to them.
- Reduce the alterations in the scope of the project as it will result in delayed deliveries.
- Closely monitor the resources costs so that the budget does not go overboard.
Conclusion
The triple constraint theory of project management is straightforward to understand and apply. Though it may sound intimidating at first glance, the principles of the triple constraint are easy. The constraints of the project are time, cost, and scope. The principle states that any changes in any constraints of the project will affect the other two.
The implication of cost is directly connected and linked to time and scope. Similarly, the reverse is also applicable. The project manager must study these interconnections and understand them. This will help him to manage the project effectively in the face of difficulties and uncertainties.
As anyone in management knows, having the right templates, plans, tools, forms and guides on hand can make all the difference in achieving success. That’s why we’ve gathered together over 9000 of the best resources available for project managers, business owners, engineers and construction employees. Whether you’re starting a new business or planning a major construction project, this comprehensive collection has everything you need to get the job done right on time.

detailed with examples, thanks for putting out this.