Agile, once lived solely in software development, aiming to speed up releases and refine features through continuous feedback loops. Now, this bold, iterative approach has leaped from tech to nearly every industry imaginable from marketing and finance to healthcare and manufacturing. The big question is: how did agile transcend its IT origins and become a driving force for modern efficiency?
In this post, we’ll explore the history of agile project management, detail its evolution beyond software, and uncover the 5 phases of agile project work. Along the way, we will describe how agile projects play out in various cross-functional settings, highlight the advantages of agile project management, and provide concrete steps that organizations can take to adopt an agile approach. Buckle up for a ride into the world of agile philosophy, where continuous improvement and adaptive planning redefine how we lead projects and define project success.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 The History of Agile Project Management & Its Evolution Beyond Software
- 3 Why Traditional Project Management Is No Longer Enough
- 4 5 Phases of Agile Project Management (And How They Differ from Waterfall)
- 5 Popular Agile Frameworks: Scrum Project Management and Beyond
- 6 Practical Application of Agile in Diverse Industries
- 7 Benefits of Agile Project Management for Modern Businesses
- 8 Action Steps to Embrace Agile Mindset Across Teams
- 9 FAQs on Agile Project Management Methodologies
- 10 Conclusion
Introduction
Purpose: Discover how agile project management (APM) techniques, once a niche approach for software development projects, now transform project management across industries. Realize why agile is seen not just as a management method but a management philosophy with a wide-ranging impact.
According to a recent survey by the Project Management Institute, revealed that 71% of organizations worldwide now use agile approaches in one form or another. Remarkably, these businesses report faster delivery times and increased responsiveness to changing market conditions.
As more sectors move away from traditional project management frameworks like waterfall, they adopt agile methodologies to stay competitive. The agile wave is sweeping through marketing campaigns, financial modeling, manufacturing, and beyond. In essence, agile has exploded outside of IT, fulfilling its promise to improve the project lifecycle by incorporating rapid Feedback and flexible scopes.
The History of Agile Project Management & Its Evolution Beyond Software
Origins of Agile and the Agile Manifesto
When discussing agile in any project management approach, it is impossible to skip its core principles, which the agile manifesto so clearly spelled out. The manifesto championed “interactions over processes and tools,” promoting swift adaptation and continuous improvement. Initially, the development process took shape in software development, where teams saw an urgent need to escape clunky, sequential project management styles.
- Agile Manifesto: The blueprint that highlights values and principles such as flexibility, customer collaboration, and rapid iteration.
- Early Adoption: Agile’s success in software development projects hinged on its capacity to incorporate user feedback throughout the project, enabling frequent changes without derailing core goals.
From IT to Cross-Industry Adoption
Agile quickly spread outside of IT. Why? The same cornerstones speed, flexibility, and early stakeholder involvement proved immensely helpful across the board.
- Facts & Examples:
- Marketing teams using scrum project management to run campaigns in sprint cycles, allowing real-time pivots based on consumer data.
- Manufacturing firms leveraging agile framework concepts to optimize supply chains and reduce lead times.
- Actionable Tip: Seek out innovative case studies, such as how a large retail chain used Scrum for in-store promotions. Sharing such stories is link-worthy and can attract referral traffic from professionals looking for fresh, agile applications.
Why Traditional Project Management Is No Longer Enough
The Difference Between Agile and Traditional Project Management
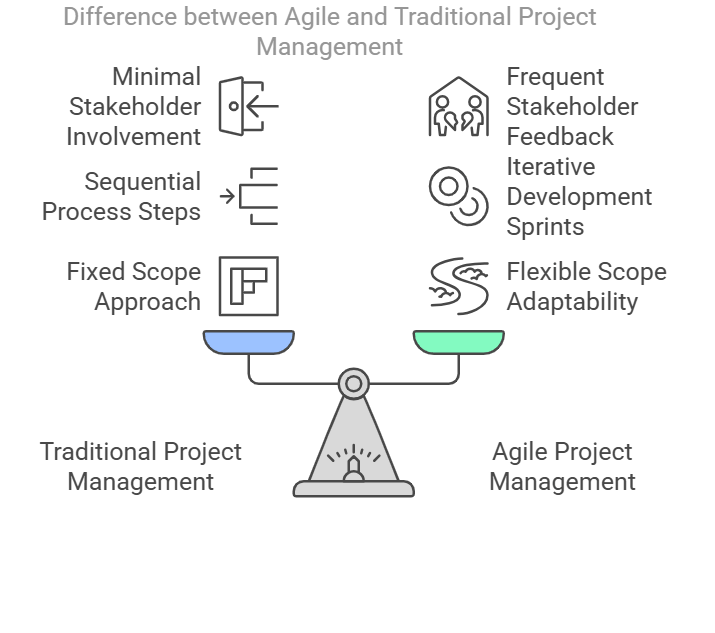
Traditional project management often relies on rigid, waterfall steps: define, design, develop, test, and deliver. While structured, this sequential project management method can falter in dynamic markets.
- Comparison:
- Agile: Flexible Scope, frequent Feedback, and iterative sprints.
- Waterfall: Fixed Scope, single end-deliverable, minimal stakeholder involvement until late in the lifecycle.
Here’s the difference between agile and older methods: agile thrives amid uncertainty, embracing evolving project requirements and stakeholder feedback throughout the process rather than in the final review. Many say agile is best for projects where speed and adaptability are crucial to project success.
The Rise of Modern Agile Management
Agile management emphasizes an agile mindset that encourages quick decision-making and robust cross-collaboration. By focusing on principles of the agile approach like welcoming changing requirements the project manager can unlock synergy in ways a top-down style often stifles.
- Embrace Agile: Make adaptability a core part of your culture, ensuring each project team is empowered to pivot.
- Project Goals: Align your project objectives with the values and principles that the agile philosophy advocates, notably delivering early and iterating often.
5 Phases of Agile Project Management (And How They Differ from Waterfall)
Note: We’ll highlight the phases of agile project management and compare them directly to waterfall approaches to illustrate why management is an iterative approach in agile contexts.
Overview of the Phases
In nearly all agile projects, you’ll encounter these five phases of agile project work:
- Initiation & Project Objectives – Define project goals and Scope at a high level.
- Planning & Backlog Creation – Translate requirements into a backlog, prioritizing tasks for upcoming sprints.
- Execution with Sprints – Implement tasks in short, time-boxed cycles, enabling Feedback from stakeholders.
- Monitoring & Adaptation – Conduct daily stand-ups, retrospectives, and frequent reviews to adapt the plan.
- Closure & Continuous Improvement – Wrap up deliverables, review lessons learned, and refine agile practices for future initiatives.
Phases of Agile Project Management vs. Waterfall
| Agile Approach | Waterfall Approach |
| Iterative (responds to change continuously) | Sequential (linear, phase-gated) |
| Frequent Feedback from stakeholders | Final Feedback Only at project’s end |
| Flexible Scope, evolves as project progresses | Rigid Scope fixed at the start |
| High Team Involvement & Collaboration | Hierarchical Control by a single authority |
Popular Agile Frameworks: Scrum Project Management and Beyond

Scrum: The Most Common Agile Framework
Scrum stands out as a scrum methodology used worldwide. It leverages clearly defined roles, rituals, and framework artifacts:
- Roles:
- Scrum Master – Facilitates scrum events and removes impediments.
- Product Owner – Prioritizes the backlog.
- Agile team – Executes tasks in each sprint.
- Artifacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and the Increment.
- Ceremonies: Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Retrospective.
By adopting Scrum, you’re effectively using a proven agile development method known for delivering results in dynamic environments. Some might say it’s the most popular project management approach in agile circles, though Kanban and Lean also hold prominent positions.
Other Agile Methodologies
Of course, Scrum isn’t the only game in town. Let’s explore more common agile options:
- Kanban: A visual workflow management system using boards, columns, and continuous flow. Sometimes referred to as Scrum and Kanban in tandem.
- Lean: A management method focused on eliminating waste and optimizing processes.
- Scaled Agile: For large enterprises running multiple agile projects concurrently.
- Comparison: Each methodology offers unique benefits, so selecting your strategy hinges on functional team structures, project scale, and the need for minimal overhead.
Agile Project Management and Scrum: Best Practices
Blend agile project management principles with scrum rituals to maximize value:
- Use an agile process to break massive goals into well-defined tasks within each sprint.
- Maintain transparency by making the backlog visible to all stakeholders.
- Encourage open communication, an approach championed by all agile methodologies.
Practical Application of Agile in Diverse Industries
Cross-Functional Teams Outside Software
Non-tech sectors also leverage agile:
- Marketing: Run campaigns in sprints to enable fast testing of ads and iteration.
- HR: Manage recruiting pipelines with Kanban boards, track daily tasks, and adapt quickly.
- Finance: Roll out budgeting cycles in iterative increments, adjusting forecasts as data emerges.
This has helped Agile deliver an application across verticals, which lets each team remain flexible over ever-changing landscapes in the marketplace.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
For many professionals, pivoting from a more traditional project management style to agile can feel daunting:
- Challenges: Fear of new management methodologies, limited training, or simply the comfort of old routines.
- Solutions:
- Run pilot programs with a smaller agile project manager and a dedicated team.
- Offer specialized training or partner with an authorized training partner program, such as a PMI Agile Certified Practitioner course or APMG Agile certification.
- Demonstrate early success to quell skepticism.
Benefits of Agile Project Management for Modern Businesses
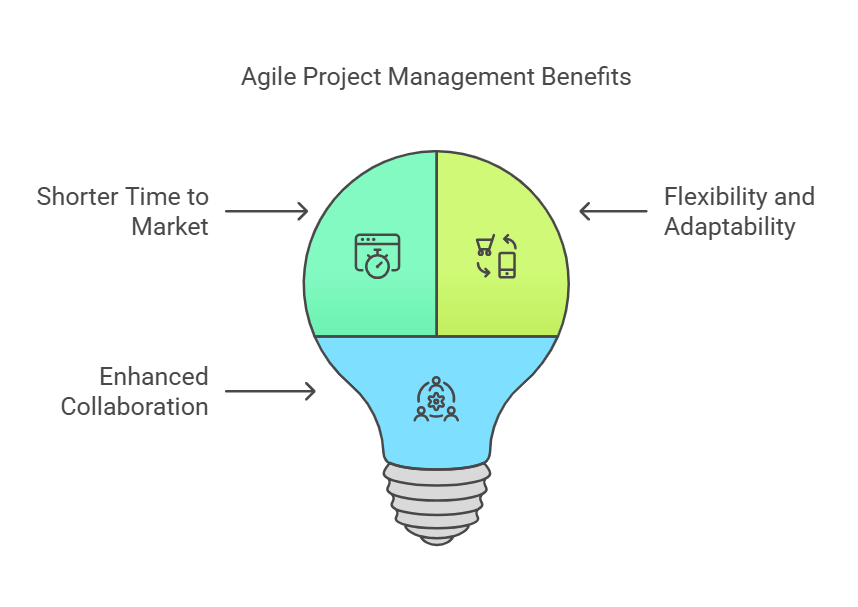
Key Benefits of Agile Project Management
Consider the benefits of agile project management:
- Shorter Time to Market: Release usable features more quickly, iterating as data streams in.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Align project objectives with fast-changing market demands, ensuring each project management cycle remains relevant.
- Enhanced Collaboration: By involving stakeholders throughout the project, you cultivate synergy and reduce miscommunication.
Agile Management for Successful Projects
Agile helps unify teams, speeds up decision-making, and fosters an environment where project management focuses on immediate feedback loops.
- Project Management Breaks Old Patterns: In agile, the hierarchical approach loosens, granting the project manager and team more autonomy.
- Management Has Become More flexible as Agile’s popularity soars, highlighting the agile way of balancing structure with creativity.
Action Steps to Embrace Agile Mindset Across Teams
Embrace Agile Through Gradual Implementation
- Pilot Project: Start with a small team, and single project management is an iterative pilot. This approach keeps the risk low while demonstrating feasibility.
- Training & Workshops: Teach principles of agile software development, encouraging teams to adopt new behaviors.
- Continuous Improvement: Emphasize retrospective discussions to refine processes, fueling the agile life cycle of learning.
Tools and Technologies
- Workflow Management Platforms: Tools like Jira, Trello, or specialized PM software accelerate communication.
- Communication Tools: Slack or Microsoft Teams for daily check-ins and sprint planning.
- Authorized Training Partner Program: The PMI agile certified practitioner path or other recognized certifications ensure best practices are followed.
FAQs on Agile Project Management Methodologies
Q1. What Is the Main Difference Between Agile and Scrum?
Answer: Agile is a broad management philosophy encompassing many methods, while Scrum is a specific scrum methodology and one of the most popular agile frameworks.
Q2. Can I Use Agile in Non-Software Projects?
Answer: Absolutely, the application of agile has expanded to fields such as HR, sales, finance, and marketing. Anywhere you can manage projects that benefit from rapid feedback loops, agile will shine.
Q3. How Do I Become an Agile Project Manager?
Answer: Obtain a scrum master certification, study the history of agile project management, and practice the principles of the agile manifesto. Joining communities, attending conferences, and continuing learning like enrolling in PMI Agile certified practitioner programs can enhance your skills.
Conclusion

Agile is a buzzword. Transcending software development and agile project management transforms the way things are handled in projects, promotes continuous improvement, and readies teams for new demands. Every industry stands to gain from an agile method of working, as agile project management and Scrum can drastically enhance project management outcomes.
As businesses embrace agile beyond IT, they discover new efficiencies, improved project success, and a dynamic culture that thrives on iterative Feedback. Why wait? Implement a pilot program today, share your progress, and become part of the global conversation about agile a conversation driving dramatic transformation across every project lifecycle.


