Contents
- 1 1. Introduction
- 2 2. Understanding ERP Integration
- 3 3. Common Types of ERP Systems
- 4 4. ERP System Integration: Everything You Need to Know
- 5 5. The Role of Emerging Technologies in Integrated ERP Systems
- 6 6. Creating a Successful ERP Integration Strategy
- 7 7. Benefits of ERP Integration & Future Outlook
- 8 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, organisations seek next-level tools to manage complexity. Enter ERP as the foundation for modern enterprise resource planning. When companies leverage ERP system integration, they unlock new business opportunities and attain a single source of truth. Yet, many remain unaware of how advanced AI, IoT, and blockchain can supercharge their ERP integration. This blog post reveals everything you need to know about unifying information and processes to create a truly integrated ERP environment so you can drive transformation in your business.
According to a 2023 Deloitte report, 74% of supply chain leaders are increasing their supply chain technology. Faster system integration is also a key motivation for adopting integrated ERP solutions. But how exactly does this synergy work? Let’s dive in.
2. Understanding ERP Integration
2.1 What is ERP Integration?
ERP integration is the process of linking ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) with different software like CRM, project management, or e-commerce to centralise business operations. Essentially, an ERP serves as management software designed to unify data across every business function.
- ERP Integration Refers: Aligning critical ERP data within a centralised ERP so that each department connects its ERP seamlessly.
- Integrated ERP Means: No more departmental silos, no more without an integrated ERP scenario, just a singular, synchronised software system that fosters collaboration and secures your most valuable datasets.
2.2 Why Integrate Your ERP System?
- The key benefits of ERP integration to Automate business processes by reducing manual tasks, duplications, and overhead.
- Enhance business intelligence with real-time analytics for inventory management, relationship management, and supply chain management.
- Without ERP integration, operational chaos emerges, leading to siloed data and misaligned business needs.
- Possible security gaps are caused by data fragments remaining scattered across legacy systems.
ERP integration can thus foster robust synergy, ensuring your entire management system can integrate swiftly and stay responsive to market changes.
3. Common Types of ERP Systems
3.1 Types of ERP & Their Characteristics
Organisations often ask: What are the types of ERP that suit different industries? Let’s examine common types of ERP:
On-Premise vs. Cloud ERP
- On-Premise: Traditional approach, housed on local servers.
- Cloud ERP: Hosted offsite, maintained by providers, ideal for agile expansion and continuous innovation.
- Cloud ERP Integration: Facilitates rapid system integration, offering real-time data updates for supply chain optimisation.
Hybrid ERP Systems
- Some companies blend the cloud ERP model with local hardware.
- This approach mitigates concerns about data control or compliance while still offering partial cloud ERP integration benefits.
3.2 Types of ERP Integrations
As your business grows, distinct ERP integration methods emerge. Types of ERP Integrations can vary:
Point-to-Point Integration
- Direct links between applications are quick but can become tangled as you add more systems.
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
- A centralised integration platform that routes data across various endpoints is less messy and more modular.
IPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
- Cloud-based: Perfect for third-party ERP integration, such as unifying CRM with your ERP or bridging e-commerce with your ERP software.
ERP Integration Scenarios
- CRM and ERP: Synchronizing marketing pipelines with finance.
- ERP and eCommerce: Linking web stores to track orders, raw materials, and shipping.
- ERP and Marketing Automation: Streamlining campaigns through one integrated ERP system.
4. ERP System Integration: Everything You Need to Know
4.1 ERP Integration Methods
ERP integration is the method that weaves these systems together. Let’s explore:
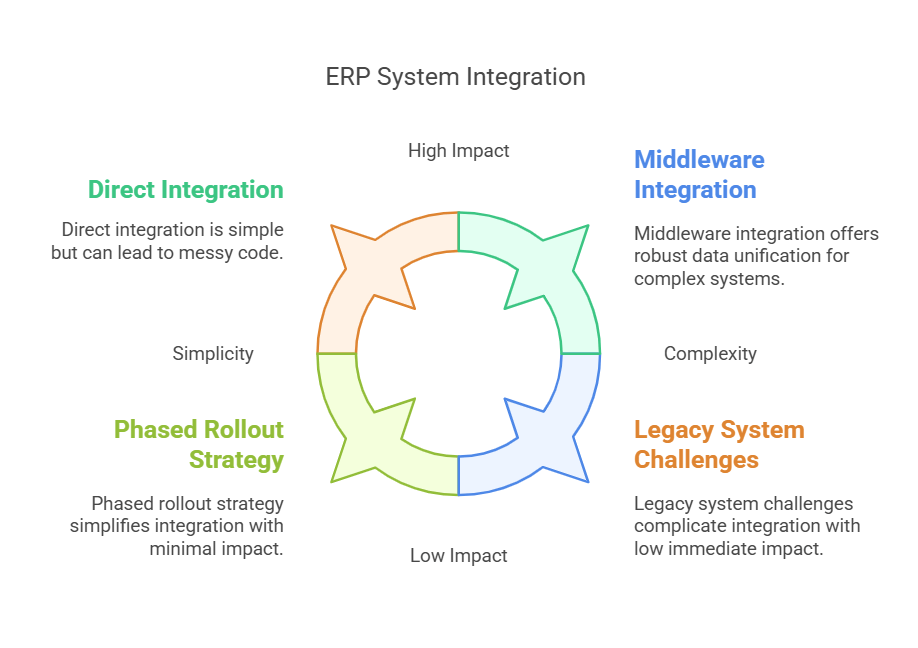
- Direct Integration vs. MiddlewareDirect Integration: Fast for smaller setups but can lead to messy code.
- Middleware: A robust “middle layer” that unifies data from software with an ERP to advanced analytics apps.
- Best Practices for ERP Integration: Start with an integration solution assessment to handle legacy systems.
- Develop a cohesive strategy-phased rollout vs. big-bang approach.
- Always ensure enterprise-grade cybersecurity during ERP system integration.
4.2 Common ERP Integration Challenges
- Data Inconsistency & Silos
- Without ERP integration, organisations risk departmental confusion; nobody sees the same data at the same time.
- Legacy Systems
- Merging older or third-party ERP tools can be tricky. However, connecting ERP with emerging technologies fosters innovation.
- Security Concerns
- Using advanced encryption, blockchain, and real-time monitoring can mitigate vulnerabilities in your ERP environment.
5. The Role of Emerging Technologies in Integrated ERP Systems

5.1 Connecting ERP with IoT
Future ERP integration with IoT and blockchain stands to revolutionise how your ERP tracks tangible assets and real-time data.
- Monitor raw materials or equipment performance with sensors that feed instant updates into your integrated ERP.
- When an organisation connects its ERP to IoT dashboards, they gain predictive analytics to enhance business operations.
ERP Systems to SaaS
- Most ERP systems depend on cloud hosting to facilitate hassle-free upgrades and ERP systems support.
- Linking your ERP system with sensor-based triggers can make maintenance schedules streamlined, reducing downtime considerably.
5.2 Blockchain for Secure Data Exchange
Blockchain isn’t just hype. It anchors your ERP data in immutable records for maximum traceability.
Supply Chain Optimisation
- Real-time ledger updates help you detect anomalies and reduce fraud, particularly in inventory management and relationship management tasks.
- This mechanism fosters trust across extended supply chain networks.
Smart Contracts in ERP
- Third-party ERP integration with blockchain can automate contract approvals and no more tedious manual checks.
- Payments, product deliveries, and compliance rules can self-execute once conditions are met, forging a frictionless process.
5.3 Agentic AI for Next-Generation ERP Integration Trends
Artificial intelligence is the generation impetus behind advanced ERP deployments.
- How Agentic AI Works is by learning from big data, adjusting business process flows on the fly by synchronising with multi-agent systems.
- This process offers dynamic insights into business needs as markets shift.
- AI-Driven System Integration Accelerates management tools usage, from finance to project management.
- Encourages new business opportunities by analysing patterns humans might overlook.
6. Creating a Successful ERP Integration Strategy
6.1 Steps to Implement an Integrated ERP System
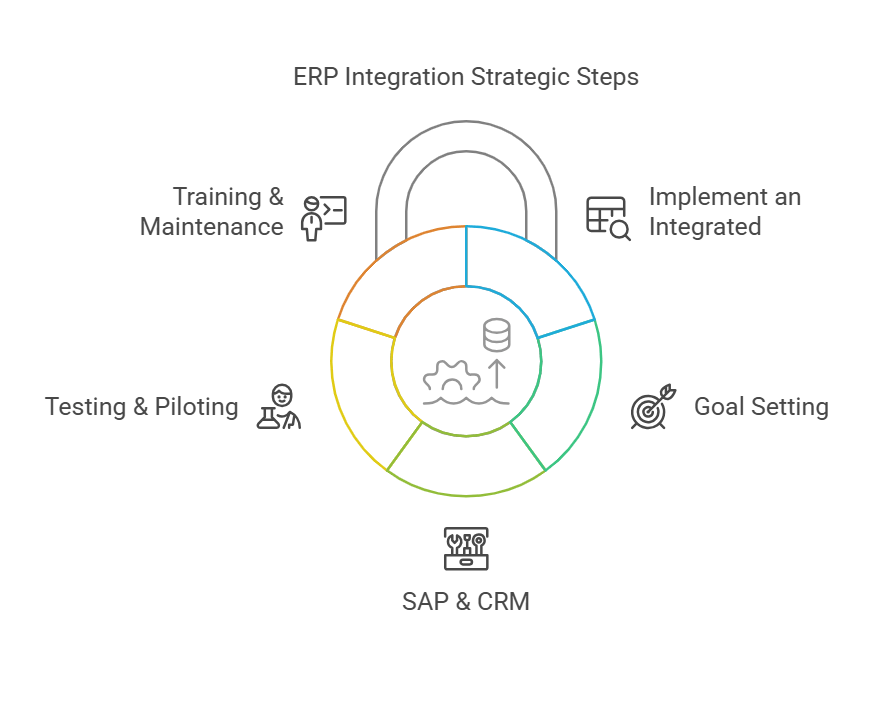
To avoid confusion and maximise ROI, consider these five action steps:
- Assess Current Infrastructure
- Identify legacy systems and pinpoint ERP systems and other applications that require immediate system integration.
- Evaluate how you can incorporate software with an ERP into a single ecosystem.
- Define Clear Goals & KPIs
- Ensure alignment on business function, data accuracy, and the overall strategy behind integrated expansions.
- Aim for a single source of truth to eliminate confusion.
- Select the Right ERP Integration Platform
- From n8n to Latenode or Kafka-based frameworks, choosing an ERP integration platform shapes your data flow.
- Compare integrated ERP solutions with third-party ERP offerings to see what suits you best.
- Pilot and Test
- Start small, maybe ERP software with other business apps or CRM with your ERP, then measure success metrics.
- Validate security and performance thoroughly before scaling.
- Train Teams & Maintain
- Ongoing training is vital to achieving a successful ERP integration.
- Regular maintenance ensures you don’t stagnate with an outdated platform.
6.2 Common Types of ERP Integration
Diverse scenarios highlight how ERP extends its reach:
SAP & CRM
- Popular for large enterprises seeking to unify supply chains with robust customer relationship management tools.
Cloud ERP & E-Commerce
- Ties your online store’s sales data to your centralised ERP, enabling quick shipping updates and real-time resource planning.
Finance & Payment Gateways
- Integrates billing, invoicing, and cost analyses under one roof so you can integrate finance data into a cohesive enterprise resource planning system.
7. Benefits of ERP Integration & Future Outlook

7.1 Benefits of ERP Integration
- Increased Efficiency
Through the implementation of an integrated ERP system, organisations are able to automate business functions and eliminate tedious manual data entry. This automation eliminates room for error, saves precious time, and permits employees to concentrate on higher-level processes that help drive innovation. Consolidating data also reduces the need for ongoing back-and-forth communication between departments, ultimately increasing overall productivity.
- Improved Supply Chain Management
An integrated ERP provides real-time visibility into raw materials, order statuses, and inventory levels. This clarity enables better supply chain optimisation, as stakeholders can foresee bottlenecks, plan logistics more accurately, and adapt quickly to sudden market changes or disruptions. Furthermore, robust insights help minimise waste, reduce costs, and enhance coordination with suppliers, carriers, and distribution centres.
- Better Decision-Making
One software system that centralises information across departments enables executives and managers to make informed decisions with increased certainty. With analysis of metrics stored in a central location, e.g., sales projections, production levels, or customer behaviour, teams can identify emerging opportunities, predict risks, and adjust strategies quickly. The shared dashboards and analytics features of an integrated ERP lower the likelihood of conflicting data sources, creating a unified perspective that helps leadership chart a clear, strategic path forward.
7.2 Future ERP Integration Trends
- AI-First Strategies
With every passing day, artificial intelligence gets more advanced, and AI-first strategies in ERP will become more common. With sophisticated machine learning algorithms, organisations can better predict demand, anticipate supply chain breakdowns, and execute mundane tasks to leave human capital free for top-level planning. AI-driven ERP can also detect hidden trends in large data sets, providing actionable insights that traditional methods can miss. These algorithms learn over time and refine their recommendations, producing increasingly accurate suggestions that can be leveraged to influence everything from inventory replenishment to customer engagement strategies.
- Blockchain-Driven Security
Blockchain technology offers an immutable ledger that bolsters data authenticity and security, making it a natural fit for ERP integration. By employing blockchain-based security, companies can cut down fraud, boost trust between supply chain partners, and guarantee that essential ERP information such as finances, origins of products, or compliance history is tamper-proof. Smart contracts, which run automatically under predefined conditions, provide another layer of efficiency. This heightened transparency not only combats data manipulation but also streamlines processes like vendor validation, payment tracking, and authentication, all while maintaining a clear audit trail.
- IoT Ecosystem Expansion
The IoT ecosystem expansion within ERP integration grants organisations unprecedented real-time visibility into their operations. Sensors embedded in machinery, vehicles, or other equipment can feed live data into the ERP system, enabling predictive maintenance and more responsive scheduling.
This interconnection assists companies in proactively eliminating bottlenecks, reducing downtime, and maximising the use of resources, ultimately reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction. As 5G and edge computing technologies become more widespread, the depth, speed, and sophistication of IoT-ERP data sharing will only increase, paving the way for increasingly agile and data-driven decision-making processes.
8. Conclusion

In conclusion, fully embracing ERP integration, whether through cloud ERP, on-premise solutions, or a hybrid model, offers a transformative strategy for unifying business operations, driving digital transformation, and staying competitive in a market that demands agility. By leveraging AI to automate workflows, tapping into IoT for real-time monitoring, and employing blockchain for secure transactions, organisations can enhance their supply chain, refine inventory management, and seamlessly integrate project management and CRM tools within a single, integrated ERP system.
This holistic approach bolsters business intelligence, cuts operational costs, and improves collaboration across departments. Ultimately, the synergy of these emerging technologies and best practices can pave the way for growth, resilience, and a future-ready enterprise, so take the leap, connect your data streams, and let a next-level ERP framework propel your business toward sustained success.
Transitioning to an integrated ERP system can feel daunting, but it also opens the door for exponential growth. By adhering to the best practices for ERP integration, you’ll unify information and processes for unmatched agility. If you integrate effectively, you’ll reduce overhead, boost productivity, and sharpen your competitive edge.
- Share and Forward: If you found this resource valuable, forward it to colleagues or partners exploring ERP applications. When you do, you help them discover the power of CRM and ERP synergy and cloud ERP integration best practices.
- Stay Updated: Keep an eye out for cutting-edge ERP systems offer updates. The global ERP market is projected to reach $117.09 billion by 2030, hinting at how quickly ERP integration is the method that continues to evolve.
By fully embracing these steps and aligning them with your business needs, you’ll be well-prepared for the generation ahead. Let the synergy of ERP guide you into a realm of efficiency, transformation, and meaningful growth.


