Contents
- 1 Introduction: The Need for ERP Security in a Digital-First Era
- 2 Understanding ERP Security: What’s at Stake?
- 3 Best Practices for Securing ERP Systems
- 4 Cloud ERP vs. On-Premises ERP: Security Challenges & Solutions
- 5 Emerging Threats & Future-Proofing ERP Security
- 6 Conclusion: Building a Secure ERP Ecosystem
Introduction: The Need for ERP Security in a Digital-First Era
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, enterprise resource planning (ERP) applications have become the pillars of today’s enterprises, and they have key functions in finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management. Although ERP systems provide the most efficient handling and streamlined procedures, they offer a profitable prize for cyberattacks, making a specialised security department essential.
Recent statistics underscore the gravity of this threat. In 2024, the global average cost of a data breach reached an unprecedented $4.88 million, marking a 10% increase from the previous year.
Alarmingly, nearly half (46%) of these breaches involved customer personal identifiable information (PII), including sensitive data such as tax identification numbers, emails, phone numbers, and home addresses.
Given that ERP systems are repositories for such sensitive information, the imperative to secure them has never been more pressing. This article delves into the prevalent threats facing ERP systems and delineates best practices to fortify them against potential breaches in line with ERP security best practices.
Understanding ERP Security: What’s at Stake?

Key Threats Facing ERP Systems Today
- Cyber Attacks on ERP Platforms: The surge in sophisticated cyberattacks, including ransomware, phishing, and brute-force intrusions, poses a significant risk to ERP systems. In 2023, malicious intrusion attempts escalated to 11.3 billion, a 6% increase from the previous year.
- Insider Threats: Employees, whether through negligence or malicious intent, can inadvertently expose sensitive data. Studies reveal that 74% of all breaches involve the human element, emphasising the need for robust internal security measures.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Third-party vendors integrated with ERP systems can introduce vulnerabilities. A staggering 40% of breaches were identified by external parties, highlighting the risks associated with supply chain security.
Common Security Vulnerabilities in ERP
- Weak Access Control: Inadequate access controls may result in unauthorised data exposure. Strong access management is important to prevent this risk.
- Unpatched ERP Systems: Neglecting timely software updates renders systems susceptible to known exploits. Regular patch management is essential to maintain system integrity.
- Data Leakage & Misconfiguration: Inadequate system configurations and the absence of encryption can lead to accidental data exposure. Secure configurations and data encryption are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data in most ERP systems.
- Inadequate Monitoring: Without real-time monitoring, it is difficult to detect and respond to breaches. Ongoing system monitoring is required to detect and respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
Best Practices for Securing ERP Systems

Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Controlling Who Sees What
Having Role-Based Access Control in place guarantees that users only have access to information required by their roles. This reduces the exposure of unauthorised data to a minimum. There must be ongoing reviewing and tweaking of access levels to ensure an ERP environment remains secure and to improve security features.
Data Encryption: Protecting Information at Rest & In Transit
Encryption of sensitive ERP information, both in transit and at rest, is critical to maintaining security standards. Using advanced encryption protocols like AES-256 and TLS 1.3 ensures that data is kept secure from unauthorised use.
Regular Security Audits & Penetration Testing
Conducting periodic security audits and penetration tests helps identify and rectify vulnerabilities within the ERP system. These proactive measures are crucial in maintaining robust security postures.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) & Single Sign-On (SSO)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification. Coupled with Single Sign-On solutions, this approach enhances security while streamlining user access.
Automated Patch Management & Security Updates
ERP systems must be updated and patched regularly to defend against identified vulnerabilities. Patch management tools with automated capabilities will be able to apply updates promptly, closing the window of vulnerability for potential exploitation in security administration.
Cloud ERP vs. On-Premises ERP: Security Challenges & Solutions

Cloud ERP Security: Is It More Secure Than On-Premise?
Cloud-based ERP systems offer benefits such as automatic updates and scalability, but they also introduce new security issues. However, they also introduce unique security challenges, including reliance on third-party security measures. Implementing a Zero Trust Security Model, which verifies every user and device, can enhance cloud ERP security.
Hybrid ERP Security: Best of Both Worlds or More Risk?
Hybrid ERP systems combine on-premises and cloud solutions, offering flexibility but also increasing complexity in integrating an ERP system. Ensuring seamless security across both environments requires integrated Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools to monitor and manage potential threats effectively.
Emerging Threats & Future-Proofing ERP Security
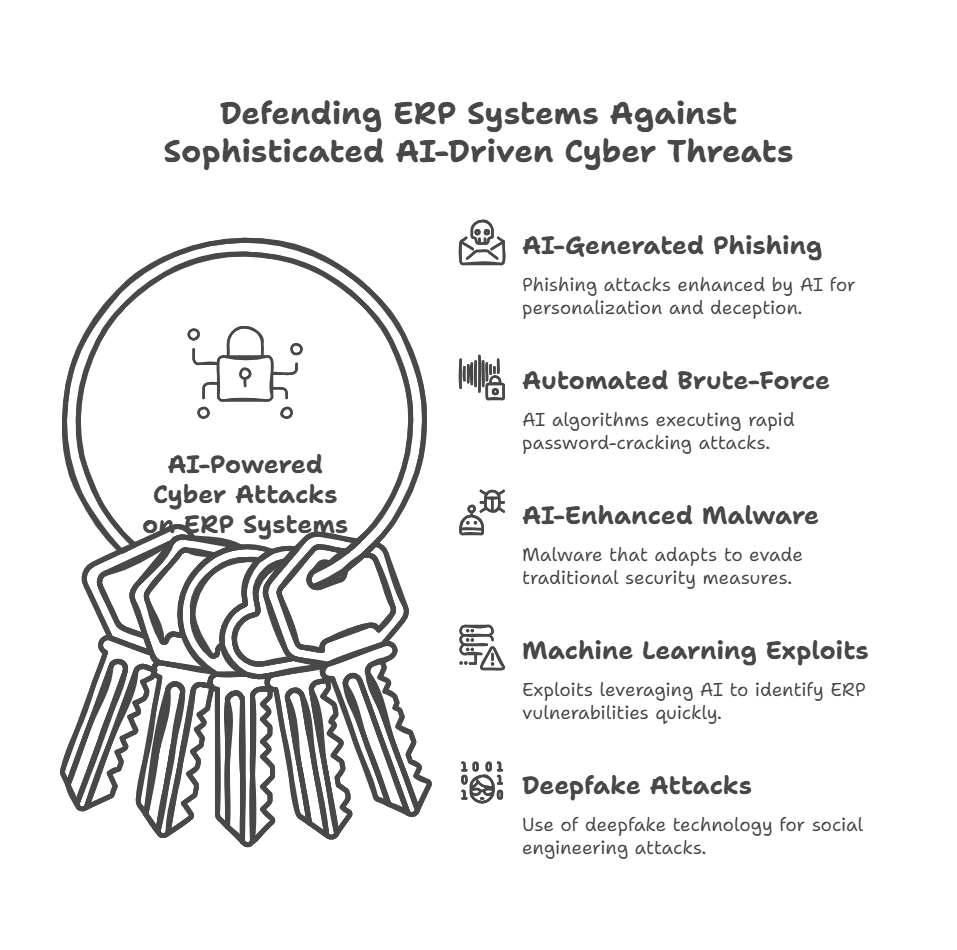
AI-Powered Cyber Attacks: The Next Big Risk?
The advent of AI-driven cyberattacks is becoming increasingly sophisticated, particularly against types of ERP systems. Presents new challenges as malicious actors leverage artificial intelligence to develop more sophisticated intrusion methods, highlighting the need for endpoint security. To counteract these threats, organisations must adopt AI-based threat detection and response systems, enabling them to identify suspicious activity in real-time.
The Growing Threat of AI-Driven Cyber Attacks on ERP Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionising cybersecurity, but it is also arming cybercriminals with more advanced tools to exploit vulnerabilities in ERP systems. Traditional cyber threats, such as those targeting ERP systems, require comprehensive security service strategies. Phishing, malware, and brute-force attacks have now evolved with AI-powered automation, making them faster, smarter, and harder to detect.
How AI Is Enhancing Cyber Threats Against ERP Systems
- AI-Generated Phishing Attacks
- AI can craft highly personalised and context-aware security features for phishing emails that imitate real communications from trusted ERP vendors, suppliers, or internal executives.
- Example: AI-driven phishing attacks targeting Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP users have increased, tricking employees into disclosing credentials.
- Automated Brute-Force Attacks
- AI-powered password-cracking algorithms can attempt millions of login combinations per second, targeting weak passwords and outdated authentication methods.
- AI-Enhanced Malware & Ransomware Attacks
- AI-driven malware learns from security defences in real time, modifying itself to evade detection by traditional antivirus software.
- AI-powered ransomware can identify and encrypt high-value ERP data within seconds, forcing organisations to pay millions to regain access.
- Machine Learning-Powered ERP Exploits
- AI can scan thousands of ERP systems across the internet, identifying unpatched vulnerabilities faster than human hackers.
- Example: AI-driven bots have significantly enhanced the capabilities of the security operations centre. Cybercriminals have exploited unpatched SAP and Oracle ERP systems to compromise the system’s security, highlighting the need for secure data practices. Preventing multi-million-dollar data breaches requires robust security service measures.
- Deepfake & Social Engineering Attacks
- AI-generated deepfake videos and voice recordings Cybercriminals often impersonate high-ranking executives to exploit security vulnerabilities within the ERP solution and authorise fraudulent transactions within ERP finance modules.
How to Defend ERP Systems Against AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
- AI-Driven Threat Detection & Response Systems
- Investing in AI-powered cybersecurity tools is essential for enhancing endpoint security in ERP systems. That analyses ERP network activity in real time, detecting anomalies and suspicious behaviour before a breach occurs.
- Example: Microsoft Defender for Cloud uses AI to advance security measures that can predict and block potential threats to the system’s security. ERP-based cyber threats.
- Zero Trust Security Model
- Never trust, always verify: Every access request to the ERP system must undergo continuous authentication and monitoring.
- Enforce multi-layer authentication protocols, including behavioural biometrics and contextual AI-based access control.
- Automated Patch Management & Threat Intelligence
- Regularly update and patch ERP software vulnerabilities before cybercriminals can exploit them.
- Utilise threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of new AI-driven attack patterns.
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) Systems
- Deploying AI-enhanced security solutions is becoming critical in addressing evolving security issues in ERP systems. Implementing security standards to monitor user behaviour can help flag unusual ERP data access. Using an ERP security solution can help prevent unauthorised transactions in real-time.
- Example: CrowdStrike Falcon uses AI to detect and block unauthorised ERP logins from suspicious locations.
- Employee Training on AI-Powered Threats
- Conduct AI-aware cybersecurity training is essential for the security staff to mitigate risks related to ERP systems. Providing training to educate employees on recognising security threats is essential for effective security management. Deepfake, phishing, and AI-manipulated ERP fraud attempts.
Conclusion: Building a Secure ERP Ecosystem

Implementing security features ensures both data security and legal adherence in ERP systems, including ERP integration. Proactive measures, continuous monitoring, and adherence to industry best practices. As ERP systems become more interconnected and cloud-based, the risks associated with implementing ERP solutions increase. Cyber threats, insider breaches, and compliance failures continue to rise. Organisations that fail to prioritise ERP security risk not only financial losses but also irreparable reputational damage.
To build a robust ERP security best practices framework. In a secure ERP ecosystem, enterprises must implement a multi-layered security approach that includes the following:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to restrict user permissions and minimise unauthorised access.
- Advanced Data Encryption (such as AES-256 and TLS 1.3) to protect sensitive information at rest and in transit, following established security policies.
- Regular Security Audits & Penetration Testing To stay ahead of AI-driven cybercriminals, it’s essential to implement security measures that address insufficient security in ERP systems.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) & Single Sign-On (SSO) to enhance identity and access management.
- Automated Patch Management to ensure timely updates and prevent attackers from exploiting outdated software.
- Zero Trust Security Models to eliminate implicit trust and continuously verify every user and device accessing ERP systems.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection & Response Systems To combat evolving cyber threats, many ERP systems are integrating advanced security management practices.
- Robust Compliance Strategies to meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 Implementing security features ensures both data security and legal adherence in ERP systems.
Final Thought: A.I – A Threat and a Solution in ERP Security
AI-driven cyberattacks pose an unprecedented risk to ERP security, but AI itself is also the most powerful tool for combating these threats. By integrating AI-powered security solutions, enforcing strict access controls, and training employees, businesses can stay ahead of AI-driven cybercriminals and protect their ERP systems from evolving threats.


