Contents
- 1 Understanding the Rise of Low-Code and No-Code in ERP Software
- 2 Key Advantages of Low-Code and No-Code ERP Customisation
- 3 Step-by-Step: How to Build an ERP with Low-Code/No-Code Development Steps
- 4 Practical Examples and Success Stories
- 5 Best Practices for a Successful ERP System Deployment
- 6 Custom ERP Benefits, Functionality, and FAQs
- 7 Conclusion
Understanding the Rise of Low-Code and No-Code in ERP Software
In today’s fast-paced market, where organisations constantly seek to drive innovation, the way we approach software development has rapidly evolved. By 2025, Gartner projects that over 70% of new business applications will be created using low-code or no-code tools. This momentum underlines how quickly both technical and non-experts can now create or customise an ERP system without complex coding.
What Is Low-Code/No-Code and Why Does It Matter for ERP?
Low-code and no-code platforms introduce a transformative shift in application development, minimising the reliance on conventional programming. They reduce the intricate coding steps into visual modules or drag-and-drop interfaces. Such user-friendly paradigms pave the way for business user engagement individuals within the organisation who understand business workflows but might not have extensive coding backgrounds.
Definition & Context
Low-code and no-code solutions simplify the software development process. This means organisations can customise an ERP system in-house, meeting specific business demands quickly. According to a recent Forrester report, low-code platforms can accelerate app creation by up to 70%.
- Why It MattersThey foster customisable ERP setups that evolve alongside changing business needs.
- They reduce the burden on specialised software developers, freeing them up for more advanced tasks.
- They lessen dependence on a single ERP vendor, giving internal teams greater autonomy to handle customisation tasks.
Traditional vs. Low-Code/No-Code Approaches to ERP Software
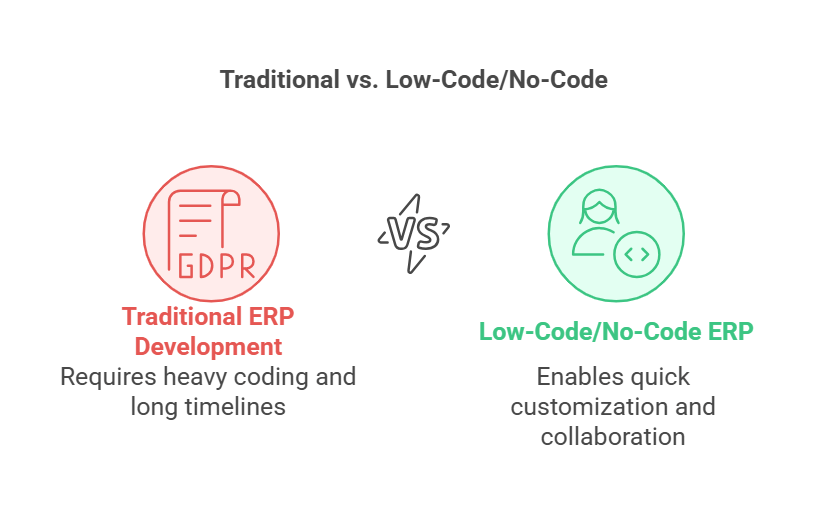
Traditional Approach
Conventionally, creating custom ERP software meant heavy coding, long timelines, and significant budget allocations. Although off-the-shelf ERP solutions can be quick to implement, they often lack the flexibility required by a unique business, leaving gaps that must be bridged by extra modules or separate apps.
Low-Code/No-Code Approach
By contrast, low-code/no-code platforms shorten development steps for new features. Collaboration becomes more fluid as business teams can directly shape the ERP system from interface layouts to automated processes without constantly needing advanced programming. This synergy between technical experts and business stakeholders results in a more customisable ERP that mirrors real business operations.
The Link Between Low-Code/No-Code and Cloud-Based ERP
Migration to the Cloud
With the growing preference for cloud-based ERP, organisations enjoy scalability, continuous updates, and accessible data. Low-code/no-code can seamlessly pair with cloud ERP platforms for constant improvements and agility in ERP implementation.
On-Premise ERP vs. Cloud ERP
Some businesses still opt for on-premise ERP to maintain direct control over their hardware and data. Yet, cloud ERP solutions such as SAP Business One, a major ERP brand, offer enhanced integration, quicker deployment cycles, and flexible expansions that align well with visual, drag-and-drop development.
Key Advantages of Low-Code and No-Code ERP Customisation

The modern business landscape prizes adaptability and speed. Low-code/no-code fosters the ideal environment by letting teams mould the ERP quickly. Let’s explore several compelling benefits.
Empowering Business Users to Customise ERP Solutions
- Faster Iterations
When business user teams play a direct role in ERP customisation, changes can be deployed swiftly. Complex coding loops are reduced, promoting rapid prototyping.
- Enhanced Collaboration
Historically, customising an ERP system meant extended back-and-forth between software developers and department heads. Now, non-technical contributors can directly customise forms, workflows, and dashboards. This approach aligns immediate business development goals with the system’s evolution.
Overcoming Common ERP Integration Issues
- Integration with Existing Systems
Many low-code/no-code platforms offer pre-built connectors to CRMs, HR tools, and other existing systems, addressing potential integration issues. If your enterprise uses specialised software or payment gateways, bridging them with your new ERP framework becomes more seamless.
- The Success of Your ERP
The smoother the integration, the less disruption to business operations. Ensuring a frictionless ecosystem can elevate the success of your ERP, thus lowering the risk of data silos or duplicated efforts.
Improving Security and Compliance with a Custom ERP System
- Addressing Security Concerns
Modern cloud-based ERP suites employ strong encryption standards and real-time security auditing. Building a custom ERP allows granular control over user roles, data access, and compliance measures, which is especially critical in regulated industries.
- Compliance Factors
A well-designed custom ERP solution can incorporate region-specific regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.), ensuring each area of business remains in line with legal norms.
Step-by-Step: How to Build an ERP with Low-Code/No-Code Development Steps
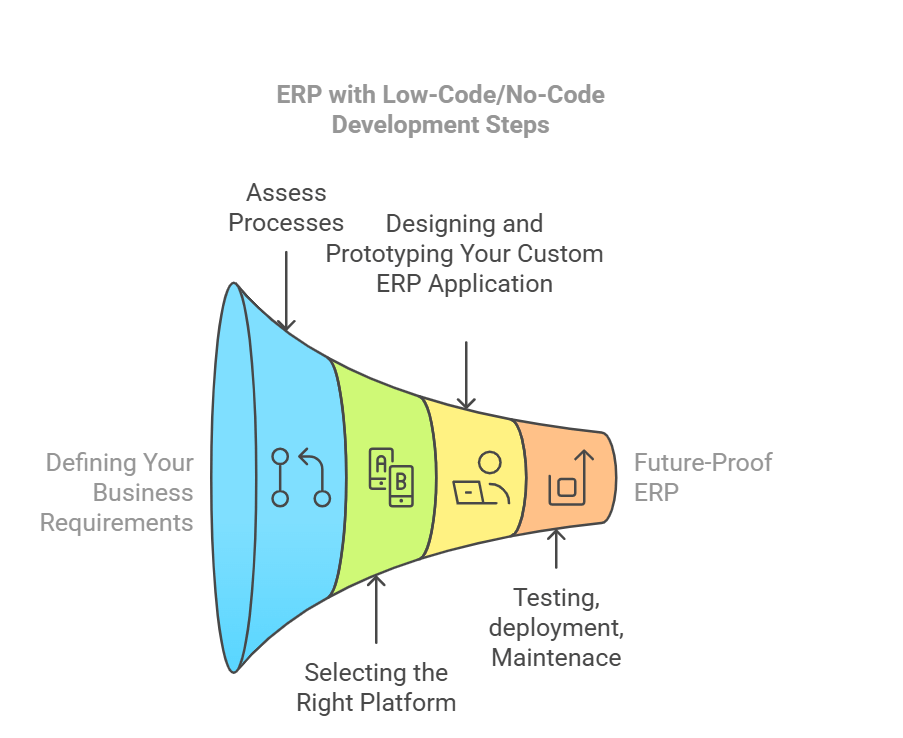
Constructing a new ERP platform may feel daunting, but modern technologies simplify the development process. Below is a roadmap featuring development steps that can turn conceptual ideas into a fully deployed ERP solution.
Defining Your Business Requirements
- Assess Business Processes
Begin by mapping your current business process automation goals. Determine which functionalities are mandatory for a customisable ERP: analytics, workflow approvals, or inventory control.
- Set Milestones
Identify each of the development steps in creating or extending your ERP system. These may include data modelling, user interface creation, and integration with third-party apps.
Selecting the Right Platform for Your Custom ERP
- Evaluate ERP Services and Vendors
Compare various ERP products, whether it’s sap-based or another competitor, and examine their capacity to support low-code or no-code. Certain ERP services specialise in easy-to-use admin consoles that are less reliant on programming.
- If needed, an ERP software development services partner or development vendor can supplement your in-house resources.
- Consider Custom ERPs vs. Common ERPA Custom ERP is an enterprise approach where everything is tailored to your business context.
- A common ERP might suffice initially but could require expensive add-ons down the line.
Designing and Prototyping Your Custom ERP Application
- User Interface and Workflow
Employ no-code modules or drag-and-drop editors to design a practical interface that aligns with your business logic. The more intuitive the layout, the more quickly your teams can adopt it.
- Application Development
Integrate low-code or advanced coding elements for specialised dashboards or complex analytics. Keep an eye on ERP implementation strategies to ensure robust testing cycles. This blend allows for the rapid creation of an ERP application that meets real business needs.
Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance
- Testing and Feedback
Gather feedback from both business and IT teams. Iterate your custom ERP functionality based on their insights.
- Deploy the Software
Whether you choose a cloud ERP or keep it on local servers, be sure to deploy the software methodically. A staged rollout helps identify bugs early while ensuring a stable go-live. Over time, your comprehensive ERP can incorporate updates seamlessly.
- Make the ERP Future-Proof
Plan expansions to keep your comprehensive ERP relevant and advanced. For instance, hooking in third-party solutions (like marketing analytics or e-commerce) ensures you’re ready for future growth.
Practical Examples and Success Stories
Sometimes, theory alone isn’t enough. Let’s showcase how organisations in different sectors have harnessed ERP solutions to reshape their business strategies.
How a Manufacturing ERP Adopted Low-Code
A mid-sized enterprise needed to revamp its production line metrics and reduce inefficiencies. Its existing manufacturing ERP couldn’t adapt quickly to new changes. By integrating low-code tools, the business was able to customise an inventory module, effectively turning it into a customised ERP that tracked resources in real time.
Adapting SAP Business One with No-Code Extensions
SAP Business One has long served SMEs needing robust ERP systems for businesses. A marketing company used no-code connectors to synchronise lead data between the ERP and its CRM in under three weeks. This shows how sap can be extended with minimal coding, ensuring real-time updates and fewer data misalignments.
Building a New ERP System from Scratch
For a cutting-edge startup with highly specific workflows, the team opted to build an ERP from the ground up, mixing low-code scaffolding with custom-coded analytics. This approach offered an opportunity to get an ERP perfectly aligned with the firm’s data demands. Through custom ERP development, they leveraged advanced reporting dashboards and predictive modelling, effectively proving that you can build ERP software tailored to even the most niche requirements.
Best Practices for a Successful ERP System Deployment

Embarking on an ERP system from scratch requires a blend of strategic planning and technical diligence. Here are some tried-and-tested strategies to ensure a successful ERP rollout.
Aligning with Business Operations and Business Efficiency
- Focus on Business Operations
Start with day-to-day tasks that frequently cause bottlenecks. An effective custom ERP must solve actual operational hurdles while promoting business efficiency.
Ensuring Security and Reliability
- Security Measures
Role-based access, data encryption, and routine audits solidify your enterprise resource planning software environment. If you want to make the ERP truly bulletproof, consider multi-factor authentication and real-time threat monitoring.
Training Non-Technical Teams
- User Adoption
By involving non-technical employees, you encourage organisation-wide acceptance of the ERP software system. Provide hands-on tutorials to show how to customise forms or modules with no-code or low-code. This approach accelerates business process automation across departments.
Engaging Software Developers for Advanced Needs
- Hybrid Team Approach
While low-code/no-code fosters quick changes, certain aspects may demand specialised coding. By uniting software developers with business leads, you’ll ensure your custom ERP software development remains stable, efficient, and innovative.
Custom ERP Benefits, Functionality, and FAQs
Detailed insights give potential adopters a clearer picture of their options. Below, we delve into custom ERP benefits, key features, and common questions.
Top Custom ERP Benefits
- Scalability
As your business scales, your ERP can also grow, adding new modules or expansions.
- Integration with Third-Party Solutions
A strong ERP easily meshes with CRM, HR, or finance systems to unify data.
- Tailored to Specific Business Needs
Why pay for unused features? A custom ERP solution focuses on what your business truly requires.
Must-Have Custom ERP Functionality
- Common ERP Modules
Finance, HR, and Supply Chain are typically part of common ERP modules. For advanced needs, you can incorporate specialised modules for niche operations.
- Core Customisation
A well-designed system includes real-time reporting, analytics, and custom ERP functionality that reflect your business roadmap.
Custom ERP FAQs
- Is a custom ERP more expensive than a common ERP?
It might have a higher initial cost, yet the long-term ROI can be greater due to efficient, pinpointed business processes.
- What about ERP Vendor Lock-In?
Opting for low-code or no-code frameworks reduces the risks of being tied to a single ERP vendor or software vendor.
- How do I start an ERP Solution from Scratch?
Evaluate ERP software development services, determine business requirements, and choose a skilled development team to craft your custom ERP system. If you prefer total control, building an ERP solution from scratch can create an ultra-tailored result.
Conclusion

Venturing into low-code and no-code approaches for ERP holds incredible promise. Indeed, ERP solutions cannot remain static; they must adapt as technology and market dynamics evolve. By focusing on the right ERP type, you can drive transformation within your organisation quickly and effectively.
These platforms empower businesses to remain agile, bridging the gap between aspiration and execution. Whether you’re looking to customise existing software or deploy the software as an entirely new custom ERP system, there’s a world of opportunity waiting for you. Embrace the potential of custom enterprise resource planning to stay ahead of the curve and gain a strategic edge in your sector.
Curious to learn more or inspired to share this software solutions guide? Spread the word to colleagues, partners, and industry peers. By forwarding this resource, you’ll build valuable networks and generate referral traffic, fueling broader discussions on the future of enterprise resource planning system innovations.


